Introduction to Load Testing Symfony
In the realm of web development, ensuring that your application can handle high volumes of traffic and maintain robust performance under varying loads is not just beneficial; it’s essential. Particularly for frameworks like Symfony, which powers a vast array of dynamic websites and applications, load testing emerges as a critical practice. This introductory section will explore the concept of load testing, underscore its significance for Symfony applications, and outline the fundamental principles that can help optimize your Symfony app to endure high traffic and provide a smooth user experience.
What is Load Testing?
Load testing is a type of performance testing used to determine a system's behavior under both normal and anticipated peak load conditions. It helps to identify the maximum operating capacity of an application, as well as any bottlenecks and elements that may cause the application to slow down or crash.
Why is Load Testing Crucial for Symfony Applications?
Symfony, a popular PHP framework for building web applications, is well-known for its ability to ensure scalability and extensibility. However, like any other framework, applications built with Symfony can face performance degradation during unexpected or high load conditions. Load testing helps to preempt such problems by:
- Identifying Performance Bottlenecks: Through simulating various usage scenarios, developers can pinpoint specific components (like database queries, APIs, or certain application functions) that may fail under stress.
- Ensuring Scalability: It verifies that the application can handle the expected number of user requests, thereby facilitating effective scaling decisions.
- Improving User Experience: By ensuring the application performs well under stress, you enhance the overall user experience, particularly during peak traffic periods.
Basic Principles of Load Testing
To successfully implement load testing for your Symfony application, keep these foundational principles in mind:
- Realistic Test Scenarios: Your load tests should mimic real-world traffic patterns and user interactions as closely as possible to generate relevant results.
- Gradual Increase in Load: Start with a small number of users and gradually increase the load. This incremental approach helps in understanding how performance issues develop as the load increases.
- Comprehensive Metrics: Collect and analyze a wide range of performance metrics such as response times, error rates, and throughput. This data is crucial for identifying potential issues.
- Continuous Testing: Load testing should be an ongoing part of your development process, especially before major releases and after significant changes to the application.
Optimizing Symfony Applications with Load Testing
Given Symfony's use of EventDispatcher, Twig templates, and Doctrine ORM, certain aspects like API endpoints, database interactions, and template rendering can become performance bottlenecks. By focusing load tests on these components, Symfony developers can ensure each part of the application architecture is optimized for high load situations.
Load testing is not just a firefighting tool; it's a necessary aspect of developing high-performing, scalable, and robust Symfony applications. By integrating regular and systematic load testing into your development lifecycle, you can preempt many performance issues and deliver a smoother, faster, and more resilient user experience. As we move forward, we will delve deeper into understanding the architecture of Symfony applications and setting up an effective testing environment.
Understanding Your Symfony Application's Architecture
Before diving into the specifics of load testing your Symfony application, it is essential to understand its underlying architecture. Symfony, a robust PHP framework for web applications, is designed around the Model-View-Controller (MVC) pattern. This architecture not only helps in organizing your application’s codebase effectively but also impacts its performance under load. In this section, we will explore the key components of a Symfony application, focusing on areas that are most susceptible to performance bottlenecks.
Core Components of Symfony Architecture
Symfony divides its functionality among several layers, each with specific roles that are crucial during load testing:
-
The HTTP Foundation: This component handles all HTTP-specific features, such as requests and responses. Understanding how your application manages these can help pinpoint areas like session management and response time issues.
-
Controller Layer: Controllers are the central part of the Symfony MVC architecture. They manage the flow of data between the server and the UI. Controllers that handle complex queries and large data sets can become performance hotspots.
-
Routing Component: Efficient URL routing is vital for a responsive application. Symfony’s routing decides which controller to run based on the URL, and performance issues may arise with complex routing rules.
-
ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) and Database Interaction: Using Doctrine ORM, Symfony interacts with databases. Performance issues often occur in the way queries are written and how data is retrieved and manipulated.
-
Template Engine (Twig): The rendering of views using Twig can also be a critical area, especially if views are data-heavy and involve complex data computations.
Identifying Key Performance Bottlenecks
To effectively prepare for load testing, you should identify components that are likely to cause bottlenecks. Common areas include:
-
Database Queries: Long-running or complex queries can severely impact performance. Tools like Symfony’s Web Profiler or Doctrine’s built-in functionalities can help you analyze and optimize these queries.
-
Session Management: Excessive session writes and reads, or large session data sizes, can slow down your application, particularly under load.
-
API Calls: External API calls that your application depends on can become a serious bottleneck, particularly if these APIs have rate limits or slow response times.
-
Caching Mechanisms: Improper use of caching can lead to redundant processing. Ensuring that your caching strategy is appropriately implemented is key to optimizing performance.
Practical Steps to Analyze Your Symfony Application
Here are a few steps you can take to better understand and prepare your Symfony application for load testing:
-
Use Symfony Profiler: This powerful tool helps you track and visualize different aspects of your application's performance during development.
-
Monitor Log Files: Regular monitoring of log files can provide insights into errors and potential bottlenecks, especially during preliminary load tests.
-
Code Reviews: Regularly review your code and database schema for potential inefficiencies that might not be evident during initial development phases.
Understanding the architecture and potential hotspots in your Symfony application is foundational for effective load testing. This knowledge not only assists in creating realistic and meaningful test scenarios but also helps in pinpointing specific areas that require optimization. Up next, we’ll cover how to set up your testing environment to simulate these user scenarios accurately using LoadForge.
Setting up Your Testing Environment
To effectively load test your Symfony application, setting up the right testing environment is crucial. This section will guide you through configuring a suitable environment using LoadForge, preparing test cases, and understanding the necessary prerequisites to ensure your testing routine is comprehensive and efficient.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have the following:
- Symfony Application: A working Symfony application set up and running locally or on a development server.
- LoadForge Account: Access to LoadForge. If you don't have an account, create one at LoadForge.
- Git: Version control to manage your codebase, especially your locustfile changes.
- Python: Ensure Python is installed, as it is required to write the locustfile scripts.
Environment Configuration
-
Isolation:
First, ensure that your testing environment is separate from your production environment. The best practice is to use a staging or development server that closely mirrors the production environment but is not in active use by real users.
-
Data Mocking:
Prepare your database:
- Use a test database that mirrors your production schema.
- Populate the database with data that mimics the production data to ensure test results are realistic.
php bin/console doctrine:database:create --env=test
php bin/console doctrine:migrations:migrate --env=test
-
Network Configuration:
- Ensure that your test server is accessible from the internet if you plan on using LoadForge's cloud service for testing.
- Check that necessary ports are open and not blocked by firewalls.
Setting Up Test Cases
To create effective test cases for your Symfony application:
-
Identify Key Scenarios:
Outline typical user paths and interactions that are critical for your application. For example:
- User Registration and Login.
- Product Browsing and Checkout Process.
- Data Retrieval and Submission Forms.
-
Determine Load Expectations:
Define what “high traffic” means for your application. Use historical data, if available, to set realistic thresholds for user numbers, request rates, and concurrency levels.
-
Convert Scenarios into Tasks for Locust:
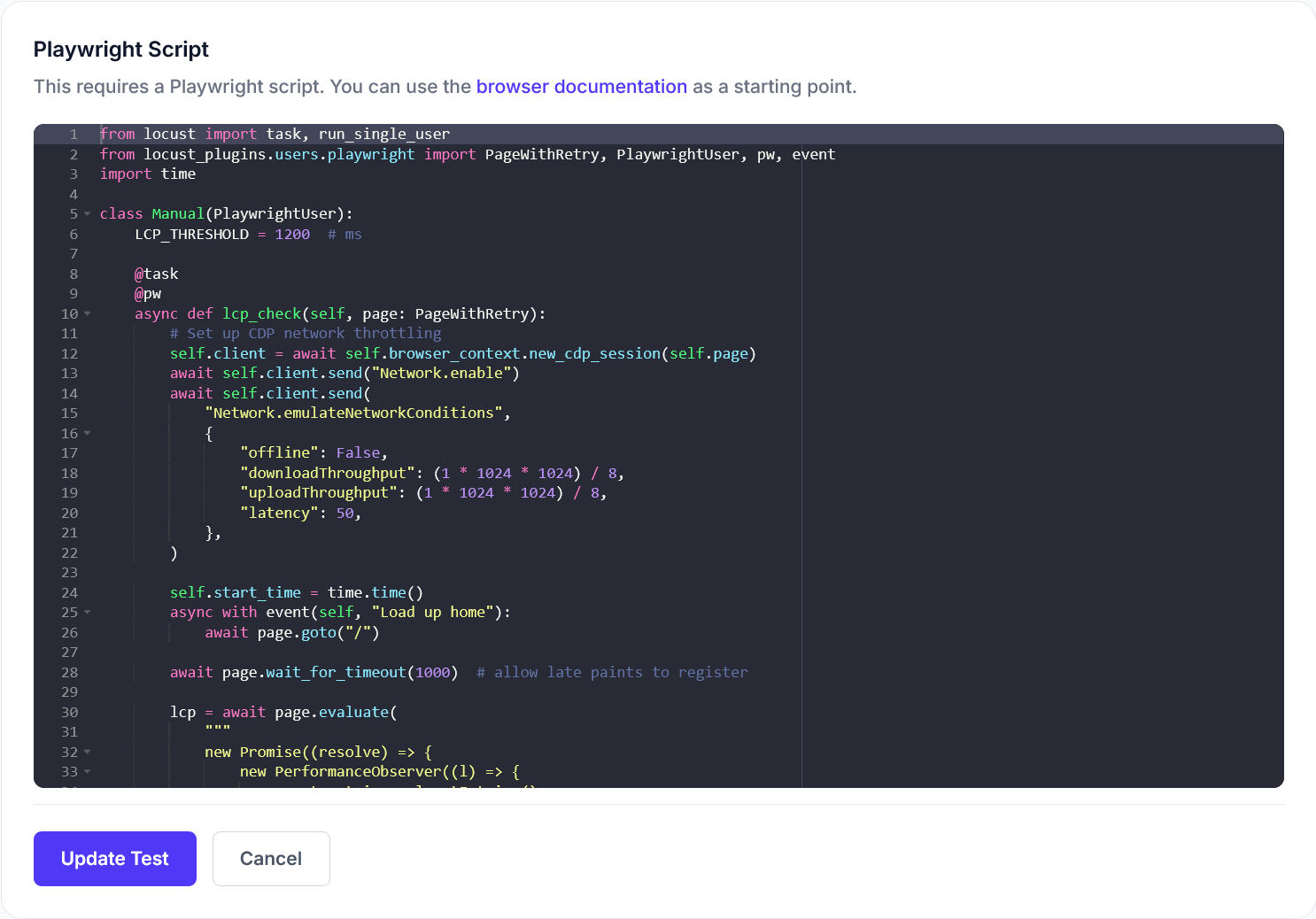
Each user scenario can be represented as a series of tasks in a locustfile. Here’s a simple example of a task simulating a user browsing products:
from locust import HttpUser, task, between
class WebsiteUser(HttpUser):
wait_time = between(1, 5)
@task
def view_products(self):
self.client.get("/products")
@task
def view_product_detail(self):
product_id = 1 # Example product ID
self.client.get(f"/products/{product_id}")
Verifying the Setup
Before proceeding with full-scale load testing:
- Run a Small-Scale Test: Start with a few virtual users to ensure the environment is set up correctly and your application is responding as expected.
- Monitor Logs: Check application and server logs for any unexpected errors or warnings.
- Resource Monitoring: Ensure the server has adequate resources (CPU, memory, network bandwidth) to handle increased loads. Tools like
htop or nmon can be useful.
Next Steps
Once the testing environment is verified:
- Move forward by uploading your locustfile to LoadForge.
- Proceed to simulate more realistic traffic patterns and evaluate how your Symfony application handles stress.
By diligently setting up a comprehensive testing environment, you lay a strong foundation for identifying and mitigating performance bottlenecks in your Symfony application.
Writing a Locustfile for Symfony
Creating a locustfile for your Symfony application is an essential step in conducting effective load testing. This section will guide you through the process of building a locustfile designed to simulate real user behavior on your Symfony web application. By the end of this section, you will have a practical example of a locustfile that tests various user interactions.
Understanding Locust and User Scenarios
Before we create a locustfile, it's important to understand what Locust is and how it operates. Locust is an open-source load testing tool that allows you to write simple Python scripts to simulate user behavior. Each simulated user has been defined in a class that inherits from User, and the tasks they perform are methods within this class.
In the context of a Symfony application, typical user scenarios might involve:
- Browsing products on an e-commerce site
- Registering a new account
- Logging in and updating account details
- Searching for items using different filters
- Checkout processes
Basic Structure of a Locustfile
A locustfile for a Symfony application typically starts with imports, followed by the definition of the user behavior classes, and concludes with the execution command if necessary. Below is a basic template that outlines this structure:
from locust import HttpUser, task, between
class SymfonyUser(HttpUser):
wait_time = between(1, 5) # Simulated users will wait 1-5 seconds between tasks
@task
def view_products(self):
self.client.get("/products")
@task
def perform_search(self):
# Assuming a search takes a query parameter
self.client.get("/search", params={"q": "example query"})
# Additional user scenarios can be added here as needed
Example: Testing a User Registration Flow
Let's focus on a common user interaction: registering a new account. Below is an example of how such a scenario could be scripted in a locustfile:
class RegisterUser(HttpUser):
wait_time = between(1, 3)
@task
def register(self):
self.client.post("/register", data={
"username": "testuser",
"password": "password123",
"email": "test@example.com"
})
This script simulates a user navigating to the registration page and submitting their details.
Complex User Behavior
In a real-world application, user behavior is more complex and might involve multiple steps that depend on responses from previous steps. Suppose we want to simulate a user who logs in, navigates to their profile, and updates some information. It could be scripted as follows:
class AuthenticatedUser(HttpUser):
wait_time = between(1, 3)
def on_start(self):
# Log in the user before performing any tasks
response = self.client.post("/login", {
"username": "existing_user",
"password": "password123"
})
self.token = response.json()['token']
@task
def update_profile(self):
# Using a token for authentication in subsequent requests
headers = {'Authorization': f'Bearer {self.token}'}
self.client.put("/profile/update", headers=headers, data={"location": "New City"})
Running Your Locustfile on LoadForge
Once your locustfile is ready, the next step is to upload and execute it on LoadForge. The next section of this guide will take a detailed look at how to do that.
By following these examples and patterns, you can effectively simulate a wide range of user interactions necessary for comprehensively load testing your Symfony application. Each scenario you script and test brings you closer to ensuring your application can handle real-world usage scenarios seamlessly.
Executing Load Tests on LoadForge
Once you have created and configured your locustfile tailored for testing your Symfony application, the next step is to utilize the LoadForge platform to execute your load tests. This process involves uploading your test script, configuring your test parameters, starting the test, and then monitoring and interpreting the results. In this section, we will guide you through each of these steps.
Uploading Your Locustfile
- Log in to your LoadForge account. If you do not have an account, you will need to create one.
- Navigate to the Tests section. Here you can manage all your test scripts.
- Create a New Test. Click on the "Create Test" button to start setting up your test.
- Upload your locustfile.
- Click on the upload section and select your locustfile from your computer.
- Make sure your file has a
.py extension and it is correctly formatted according to LoadForge's requirements.
Configuring Test Parameters
After uploading your locustfile, you need to set the parameters for your load test:
- User Simulation: Decide how many simulated users you wish to run (this represents concurrent users).
- Spawn Rate: Determine the rate at which new users are simulated per second.
- Test Duration: Specify the duration for which the test should run.
These parameters can be adjusted based on the specific load you want to test your application under. For high-traffic websites, you might start with a large number of users to see how well your application responds to extreme stress.
Starting Your Load Test
With your locustfile uploaded and your test parameters set, you can begin your test:
- Review your settings, ensuring everything is configured correctly.
- Launch the test by clicking the "Start Test" button.
- LoadForge will distribute the execution across its cloud infrastructure based on the specified requirements.
Monitoring Performance in Real-Time
Once the test begins, LoadForge provides a real-time dashboard where you can monitor the progress and performance of your load test:
- User Statistics: Track the number of users simulated over time.
- Response Times: Monitor how quickly your Symfony application is responding under load.
- Error Rates: Keep an eye on any errors that occur during the testing process.
Interpreting the Results from the LoadForge Dashboard
After the test concludes, the dashboard will display a detailed report of the performance metrics:
- Response Time Graphs: Analyze how response times varied during the test at different levels of load.
- Error Overview: Review any errors encountered and identify potential causes within your Symfony application.
- Resource Usage: Observe the usage stats for server resources during testing to identify potential hardware limitations.
Sample Analysis:
- Look for trends in performance degradation as user load increases.
- Identify the response time thresholds where your application performance begins to falter.
- Use error logs to trace back to specific parts of your Symfony application that may need optimization.
By carefully analyzing these results, you can gain valuable insights into the scalability and robustness of your Symfony application. This process is crucial for preparing your application to handle real-world traffic scenarios effectively.
Analyzing Test Results and Optimizing Performance
After successfully executing load tests on your Symfony application via LoadForge, the next critical step is to analyze the results to understand the performance under stress and identify any potential bottlenecks. This section will guide you through the analysis of test outcomes and provide strategic approaches to optimizing your application for better performance and scalability.
Interpreting Load Test Data from LoadForge
Once LoadForge completes the load testing, it provides you with a comprehensive dashboard showing various metrics. Key metrics to look closely at include:
- Response Time: How quickly your application responds to requests during the test. Look for increases in response time as the load increases, which can be a sign of bottlenecks.
- Requests Per Second: The number of requests your application can handle per second. A drop in this number can indicate performance issues.
- Error Rate: The percentage of failed requests. High error rates may suggest problems in specific parts of your application.
- Resource Utilization: CPU, memory usage, database connections, and other system resources. Spikes or high usage can indicate insufficient resources or inefficiencies in code.
Analyzing Performance Trends
Use LoadForge's graphs and reports to track how these metrics change over time and under different loads. Look for:
- Trends where performance metrics degrade gradually or suddenly.
- Points where the application fails to respond or error rates spike.
This analysis will help you pinpoint parts of your application that are less scalable or need optimization.
Identifying Bottlenecks in Your Symfony Application
Typical areas in Symfony applications where bottlenecks manifest include:
- Database queries: Long or complex queries can slow down your application. Use Symfony's built-in profiler or tools like Symfony Insights to identify slow queries.
- External API Calls: Calls to external services can delay response times. Ensure these are optimally managed or cached when possible.
- Route and Controller Logic: Inefficient logic in controllers or heavy operations within routing can significantly delay responses.
To dive deeper, you might use the profiling data to view specific requests that took longer times and examine the execution workflow within your code.
Optimizing Your Application
Once bottlenecks are identified, focus on enhancing these areas:
-
Optimize Database Interactions:
- Use indexing for faster query processing.
- Optimize queries or use a query builder to ensure efficient data retrieval.
- Consider implementing read replicas for heavy read operations.
-
Cache Content:
- Utilize Symfony's caching mechanisms to store parts of your web pages or API responses that don't change often.
- Use a distributed cache system like Redis for high-efficiency caching.
-
Asynchronous Processing:
- Implement asynchronous tasks for operations that are resource-intensive and don't need to be done within the user request cycle, like sending emails or processing files.
-
Code Profiling and Refactoring:
- Regularly profile the code to find inefficient methods or classes.
- Refactor code for better performance, adhering to Symfony's and general PHP best practices.
-
Scaling Your Infrastructure:
- Based on the test results, decide if scaling vertically (more powerful servers) or horizontally (more servers) is needed.
- Look into load balancers and clustering solutions to distribute the load evenly.
Conclusion
Regularly repeating the load tests after making optimizations and during the development cycle ensures that your application remains resilient under high traffic conditions. By continuously analyzing and optimizing, you ensure that your Symfony application is not only stable and scalable but also provides a robust user experience regardless of load.
By taking a structured approach to analyzing LoadForge test outcomes and optimizing your application, you significantly improve the performance and scalability of your Symfony applications.