Introduction to Load Testing Drupal
Load testing is an essential practice for any website, particularly for dynamic content management systems like Drupal. By simulating multiple users accessing your website simultaneously, load testing helps reveal how your Drupal site will perform under stress before it impacts actual users.
Why Load Testing is Crucial for Drupal Websites
Drupal is a highly popular open-source content management system known for its flexibility and robust functionality. While these features make it a preferred choice for many enterprises, they can also make Drupal sites susceptible to performance issues if not properly optimized. Here's why load testing is particularly important for Drupal websites:
- Complexity and Scalability: Drupal's ability to handle complex sites with various modules and themes can lead to unexpected strains on web servers as traffic increases.
- User Experience (UX): Slow loading times and poor response rates can frustrate users, leading to a higher bounce rate and reduced engagement.
- SEO Impact: Search engines, like Google, prioritize site speed as a key factor in their ranking algorithms. Performance delays can result in lower search rankings.
- Infrastructure Assessment: Regular load testing helps assess whether your current hosting solution can handle peak traffic periods, especially important for high-traffic events or campaigns.
Benefits of Regular Load Testing
Regular load testing offers several tangible benefits that help maintain and enhance the health of a Drupal site:
- Identifying Performance Bottlenecks: Determine which parts of your site (e.g., specific modules or features) degrade its performance as the load increases.
- Validating the Scalability of Your Site: Understand how well your Drupal site can scale with increased traffic, and identify the threshold at which the performance starts to degrade.
- Improving User Retention: By ensuring that your site can handle high traffic volumes smoothly, you can provide a better user experience, leading to higher retention rates and more successful user interactions.
- Cost Management: Load testing provides insights that help decide if you need more robust hardware or if optimizations can defer additional hardware expenses.
Conclusion
Load testing is not just a safety measure but a proactive tool that can significantly improve the effectiveness of a Drupal website. As traffic grows and the complexity of your Drupal site increases, regular load testing becomes imperative to ensure your site remains fast, efficient, and capable of delivering the best possible user experience.
Understanding the Architecture of Your Drupal Site
Before stepping into the tangible phases of load testing your Drupal website, it’s pivotal to grasp the architectural nuances that constitute your site. Drupal, being a robust content management system, integrates various components that could influence its performance under varying load conditions. This section deciphers the usual setups such as databases, caching solutions, and third-party integrations which play a significant role in your site's responsiveness and scalability.
Key Components of a Drupal Architecture
1. Database
Drupal uses a database to store website content, configuration settings, user information, and other critical data. The choice of database and its configuration can significantly impact the performance of your Drupal site. Common databases used with Drupal include:
- MySQL/MariaDB: The most widely used database with Drupal installations.
- PostgreSQL: Known for its robustness and used by those preferring this technology over MySQL.
- SQLite: Generally used for testing or smaller applications due to its simple setup and minimal configuration requirements.
Ensuring that the database is properly optimized, such as adjusting the caching mechanisms and indexing, is crucial for reducing load times and improving overall site performance.
2. Caching
Efficient caching can drastically reduce the load on your Drupal site by storing copies of files or pieces of data to serve future requests directly from the cache. This reduces the need to regenerate dynamic content. Drupal typically includes several layers of caching:
- Page Caching: Stores the entire HTML output of a page. Effective for anonymous traffic as it reduces database load significantly.
- Block Caching: Caches the output of rendered blocks that are used to build Drupal pages.
- Entity Caching: Entities like nodes, users, and terms can be cached to speed up their load times.
- Views Caching: Specific for views, which are queries made to display lists and tables of content.
Configuring and managing these caches according to your traffic patterns is a foundational aspect of optimizing your Drupal site’s performance.
3. Third-party Integrations
Drupal's extensibility through modules means that many sites utilize third-party integrations for various functionalities, from SEO tools and social media feeds to complex business applications. Each integration introduces potential overhead and could impact performance. Key considerations include:
- Web services: RESTful APIs, SOAP calls, and external data fetches which if not optimized, can lead to significant delays.
- JavaScript/CSS aggregation: External resources should be minimized and aggregated to reduce the number of HTTP requests.
Understanding the overhead introduced by these integrations is crucial for accurate load testing and further optimization.
4. File System
The file system in Drupal is used for storing uploaded content and other files. Performance can be influenced by the:
- Choice of file storage: Local storage vs. CDN or external storage solutions.
- File handling modules: Such as Image Styles which can generate multiple resized images on demand.
Handling large volumes of file data efficiently is crucial, especially for media-rich Drupal sites.
Diagnosing Your Current Setup
Before advancing into load testing, evaluate your current Drupal setup by:
- Analyzing the environment: Including server type, PHP configuration, database settings, and installed modules.
- Identifying potential overload points: Such as complex views, uncached blocks, or poorly optimized queries.
- Monitoring initial performance metrics: Using tools like Drupal’s built-in performance logging or web-based services to get a baseline of your site’s performance.
Understanding these aspects of your Drupal architecture will allow you to tailor your load testing setup more precisely, ensuring that the tests are meaningful and that the solutions you implement effectively enhance the performance of your site.
Setting Up Your Load Testing Environment
Before diving into the actual load testing of your Drupal site, setting up a proper testing environment is critical. This environment should mimic your production environment as closely as possible to obtain accurate results. This section will guide you through establishing a basic load testing setup using LoadForge, selecting the test scale, choosing locations for load generation, and emphasizing the importance of a production-like environment.
Selecting the Scale of the Test
The scale of your load test defines the intensity and scope of the simulated traffic to your Drupal site. Here are factors to consider:
- Expected Peak Traffic: Estimate the maximum number of users your site might receive during peak times and set your tests to simulate slightly above this number.
- Growth Projections: Consider any expected increases in traffic due to marketing campaigns, new feature releases, or business growth over time.
- Resource Limitations: Account for the resources available in your LoadForge account, such as maximum concurrent users and rate limits.
To set the scale in LoadForge, define the number of users (User count) and the spawn rate (Spawn rate), which controls how fast the users will hit your server:
from locust import HttpUser, task, between
class WebsiteTest(HttpUser):
wait_time = between(1, 5)
@task
def index_page(self):
self.client.get("/")
Choosing Locations for Load Generation
LoadForge allows you to generate load from multiple geographic locations, enabling you to understand how your Drupal site performs for users in different parts of the world. Considering geographic diversity is crucial for global businesses to ensure a consistent user experience worldwide.
To set up different geographies, navigate to the LoadForge test creation dashboard and select your desired regions. This feature allows you to test the responsiveness and speed of your Drupal site across various network conditions and distances.
Importance of a Production-like Environment
Testing in an environment that closely replicates your live Drupal site is paramount. This approach minimizes variables between the testing and production environments, leading to more reliable and relevant results. Consider the following when setting up your environment:
- Hardware and Infrastructure: Use servers, network configurations, and hardware specs similar to your production environment.
- Software Configuration: Align your Drupal configurations, modules, third-party integrations, and databases with your live site.
- Data Volume: Utilize a dataset that mirrors the size and complexity of your production data.
Here is an example configuration on LoadForge for setting environment variables, which can be crucial for replicating production settings:
environment = {
'DB_HOST': 'production_db_host',
'API_KEY': 'production_api_key'
}
By following these guidelines, you establish a robust foundation for load testing your Drupal site using LoadForge. The next steps include creating specific test scenarios and running the tests, which we will cover in the following sections of this guide.
Creating Your First Locustfile for Drupal
In order to effectively load test your Drupal site, you will need to script realistic user scenarios that reflect typical interactions with your website. This involves crafting a locustfile, a Python script that defines user behavior. In this section, we will guide you through writing a basic locustfile that simulates common activities such as logging in, browsing pages, and submitting forms.
Step 1: Set Up Your Locust Environment
Before you start coding, ensure you have Python installed on your machine and install the Locust framework with the following command:
pip install locust
Step 2: Define User Behavior
A locustfile is essentially a Python script. Below is an example of what your basic locustfile might look like when targeting a Drupal website.
from locust import HttpUser, task, between
class DrupalUser(HttpUser):
wait_time = between(1, 5)
def on_start(self):
""" Perform tasks to run before any task is executed. """
self.login()
def login(self):
""" Simulate user login sequence."""
response = self.client.post("/user/login", {
"name": "example_user",
"pass": "example_password",
"form_id": "user_login_form"
})
if response.status_code == 200:
print("Login successful")
else:
print("Login failed")
@task
def browse_pages(self):
""" Simulate browsing different pages."""
pages = ["/node/1", "/node/2", "/about-us", "/contact"]
for page in pages:
self.client.get(page)
print(f"Browsed {page}")
@task(3)
def submit_form(self):
""" Simulate submitting a form."""
self.client.post("/form-handler", {
"name": "John Doe",
"email": "john@example.com",
"message": "Hello, this is a test message!"
})
print("Submitted form")
Step 3: Understanding the Code
-
Class Definition: The class DrupalUser extends HttpUser, which provides the functionality to make HTTP requests.
-
Wait Time: wait_time = between(1, 5) randomly waits between 1 to 5 seconds between different tasks to simulate real user behavior.
-
on_start Method: This method is called when a simulated user starts executing. It is typically used to perform login operations.
-
Tasks: Defined with the @task decorator. The optional argument (like @task(3)) increases the weight of the task, making it more frequent. Each method simulates a different aspect of user interaction.
Step 4: Running Your Test
To run your test:
- Save the above script as
locustfile.py.
- Open your terminal and navigate to the directory containing
locustfile.py.
- Run the command:
locust --host=http://your-drupal-site.com
- Open a web browser and go to
http://localhost:8089 to access the Locust web interface.
- Enter the number of users to simulate, the spawn rate, and start swarming.
Conclusion
By following these steps, you will have created a basic locustfile capable of simulating a user logging into a Drupal site, browsing pages, and submitting forms. This setup provides a foundation for further customization and complexity as you expand your load testing scenarios to cover more aspects of your Drupal site's functionality.
Advanced Scenarios and Customizations
As your Drupal site begins to scale, and as user interactions become more complex, it's vital to evolve your load tests to address these changes. Advanced scenarios in load testing help simulate more realistic high-traffic situations and incorporate custom scripts to mimic real-user interactions closely. This section details how to enhance your locustfiles for more complex load testing scenarios using the LoadForge platform.
Simulating High Traffic
When your Drupal site grows, it's critical to understand how it will perform under significant stress. High traffic simulation involves creating multiple user scenarios that vary in intensity and type of interactions. Here’s how you can scale your locustfiles to mimic such environments:
-
Increase the Number of Users:
Scale the number of simulated users gradually to observe how the system behaves under increased load. You can adjust the number of users directly in your locustfile:
class UserBehavior(TaskSet):
@task
def view_pages(self):
self.client.get("/")
class WebsiteUser(HttpUser):
tasks = [UserBehavior]
min_wait = 5000
max_wait = 9000
host = "https://yourdrupalsite.com"
# Simulation for increased number of users
scale_to = 5000 # Scale up to 5000 users
-
Vary User Behavior:
Real-world users don't follow a single pattern. Some might be browsing, while others could be interacting with forms or accessing different services. Implement varied user paths in your locustfiles:
@task(3)
def browse_products(self):
self.client.get("/products")
@task(1)
def post_comments(self):
self.client.post("/comment/submit", {"comment":"Great product!"})
Using Custom Scripts
To further close the gap between simulated tests and real user interactions, custom scripts can be used. Custom scripts allow you to simulate more detailed user behavior, including complex sequences of actions and the handling of JavaScript-rendered content.
-
Sequential Tasks:
Users often perform actions in sequences, such as logging in before making a purchase. Use Locust's SequentialTaskSet for this purpose:
from locust import SequentialTaskSet, task, HttpUser
class UserSequence(SequentialTaskSet):
@task
def login(self):
self.client.post("/login", {"username":"user", "password":"passwd"})
@task
def purchase_item(self):
self.client.post("/buy", {"product_id": 123})
class WebsiteUser(HttpUser):
tasks = [UserSequence]
-
Handling AJAX and JavaScript:
If your Drupal site heavily relies on AJAX calls or JavaScript, consider simulating these aspects in your test. You can capture AJAX requests from your site's network traffic (using tools like Chrome's Network Inspector) and replicate them in your locustfile.
Performance Tips for Advanced Testing
- Monitor your tests closely: As you implement more sophisticated tests, closely monitor the performance and resource utilization to avoid overloading your test environment.
- Increment test complexity gradually: Start with basic scenarios and progressively incorporate more complexity to ensure your system can be accurately evaluated at each stage.
- Iterate based on feedback: Use the insights gained from each test run to tweak scripts, adjust user simulations, and refine your approach for greater accuracy.
By following these advanced strategies, you can ensure that your Drupal site not only sustains high traffic but also delivers an optimal user experience during peak times.
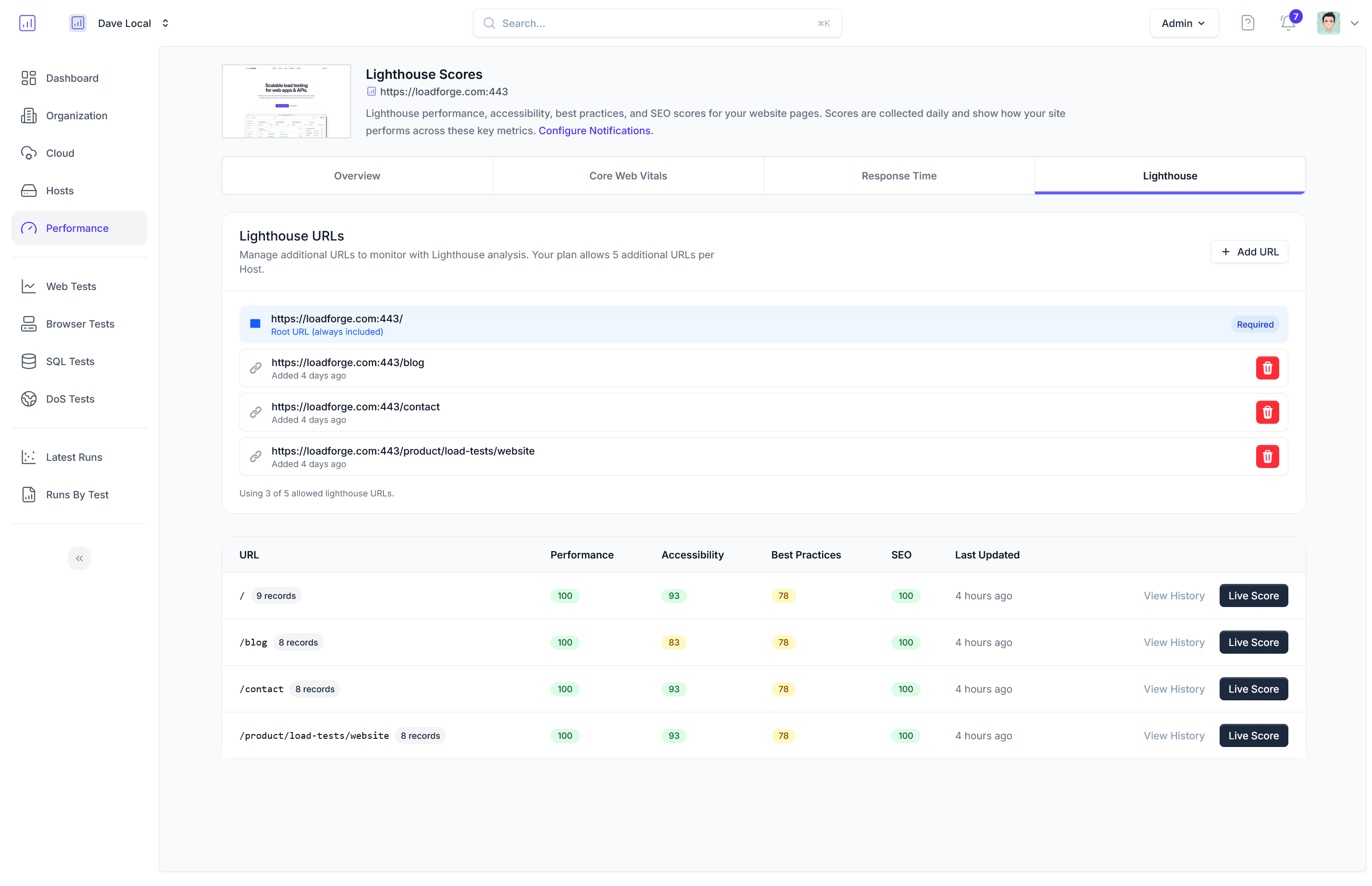
Analyzing Test Results and Identifying Bottlenecks
After executing a load test on your Drupal site using LoadForge, the next crucial step is analyzing the gathered data to understand the performance implications and identify any potential bottlenecks. This section provides a comprehensive guide on interpreting LoadForge test results, with a focus on metrics such as response time, failure rate, and concurrent users.
Understanding Key Performance Metrics
-
Response Time: This is the time taken for a request to be processed and the response to be sent back to the user.
- Average Response Time: Provides a general idea of the delay users might experience.
- Maximum Response Time: Indicates the worst-case scenario, which is critical for understanding the highest potential delay a user might face.
- Percentiles (e.g., 95th, 99th): These values help in understanding the distribution of response times across all users. The 95th percentile, for example, shows the maximum response time experienced by 95% of the users, which helps in identifying outlier behaviors.
-
Failure Rate: Measures the percentage of requests that did not succeed.
- High failure rates can be indicative of server errors, capacity issues, or other critical problems that need immediate attention.
-
Concurrent Users: Refers to the number of users interacting with your site at the same time during the test.
- Monitoring how the site performs under varying levels of concurrent users is essential for determining at what point the performance starts to degrade.
Steps for Analyzing Test Results
-
Review the Load Testing Summary:
- Start by looking at the summary dashboard provided by LoadForge, which highlights the key metrics at a glance.
-
Dive Deep into Response Times:
- Analyze the response time graphs and logs to pinpoint when and why slowdowns occur. Look for patterns or specific times when the performance drops.
-
Examine Failure Rates:
- Identify when the failure rates spike. Correlate these spikes with changes in load patterns, response times, or other observable metrics.
-
Assess Performance Against Concurrent User Loads:
- Evaluate how the response time and failure rate change as the number of concurrent users increases. This analysis helps in understanding the scalability of your Drupal site.
Identifying Bottlenecks
Once you have a clear understanding of the metrics, the next step is to identify the bottlenecks. Here are some common areas to investigate:
- Database Performance: Long query times can severely impact the response times.
- Server Resources: CPU and memory limitations on your server can also be a major bottleneck.
- Network Issues: Poor network performance can affect the load times, especially with higher user concurrency.
- Application Code: Inefficient loops, algorithms, and unoptimized code can slow down the application.
Tools and Commands for Further Investigation
You might need to delve deeper into specific issues identified during the load test. Here are some tools and commands that can be useful:
# Monitoring CPU and Memory usage
top
# Analyzing network traffic
netstat
# Database performance monitoring
EXPLAIN ANALYZE SELECT * FROM my_table;
By thoroughly analyzing the load test results from LoadForge and investigating the identified bottlenecks, you can significantly enhance the performance and scalability of your Drupal site. Remember, the goal is to ensure a seamless and efficient user experience even under high traffic conditions.
Optimizing Drupal Performance
After conducting thorough load testing on your Drupal site using LoadForge, you've likely identified several performance bottlenecks. This section discusses practical, actionable strategies to enhance the performance of your Drupal website. By implementing these optimizations, you can significantly improve the responsiveness and scalability of your site, ensuring a better user experience during peak loads.
Implement Advanced Caching Mechanisms
Caching is critical in Drupal to reduce the load on the server and speed up the page delivery. Drupal provides several layers of caching which can be configured to optimize performance:
-
Page Caching:
Full page caching can dramatically reduce the response time for anonymous users. Ensure it's enabled under /admin/config/development/performance.
-
Views Caching:
For sites heavily utilizing views, enabling caching for each view can have a substantial impact. Configure this in the advanced settings of each view.
-
Block Caching:
Enable block caching by visiting each block configuration and setting the appropriate cache level.
-
Browser Caching:
Leverage browser caching by setting appropriate Expires headers and Cache-Control directives in your .htaccess file.
Optimize the Database
The database is often the bottleneck in high-traffic Drupal sites. Optimizing your database can improve response times and support higher loads:
-
Indexing:
Regularly review your database queries and ensure that all frequently queried fields are indexed appropriately.
-
De-normalization:
Sometimes it's beneficial to de-normalize your database to reduce the complexity of queries.
-
Query Optimization:
Use the Devel module to identify slow queries and refactor them for better performance.
-
Database Maintenance:
Regularly perform maintenance tasks such as clearing old session data and optimizing tables.
Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
Serving your static assets (images, JavaScript, CSS) from a CDN can greatly reduce the load on your servers and speed up content delivery worldwide. Configure CDN integration by using the CDN module for Drupal which redirects the static asset URLs to your CDN provider.
Optimize Files and Image Handling
Images can significantly affect the load times. Optimize how images are handled:
-
Image Styles:
Predefine image styles to scale images server-side before delivery, reducing file sizes.
-
Lazy Loading:
Implement lazy loading to defer loading images until they are in the viewport.
Tweak Drupal’s Performance Settings
Drupal has built-in performance settings that can be tweaked:
/admin/config/development/performance
Adjust these settings for:
- CSS and JavaScript Aggregation: Enable to reduce the number of HTTP requests.
- Render Cache: Use to cache renderable arrays, entities, and pages, decreasing the rendering time.
Regularly Update and Audit Modules
Keep your Drupal core and all modules updated to benefit from optimized code and security enhancements. Additionally, audit and remove any modules that are no longer in use or replace heavy modules with lighter alternatives.
By implementing these strategies based on your LoadForge load test results, you should see significant improvements in the performance of your Drupal site. Regular monitoring and tweaking will keep your site optimized and ready to handle varying loads efficiently.
Continuous Integration and Regular Testing
Load testing is not merely a task to be checked off during initial development stages; it is an ongoing process that should be integrated into the regular operational cycle of your Drupal website. Incorporating LoadForge tests into your continuous integration (CI) pipeline ensures that your site remains robust, scalable, and responsive under varying loads, thereby safeguarding user experience and ensuring system stability. This section provides a step-by-step guide on how to integrate LoadForge load tests into your development workflow, making regular testing and evaluation a fundamental part of your practice.
Integrating Load Testing into Your CI/CD Pipeline
Integrating LoadForge with your CI/CD system can be accomplished with several automated steps. Here's how you can set it up:
-
Create Load Test Scenarios:
Begin by writing or updating your locustfile.py to simulate user interactions on your Drupal site. This includes actions like page navigation, form submissions, user authentication, and more.
-
Configure LoadForge:
Set up a LoadForge test using your locustfile. Define the scale, duration, and frequency of the test according to your requirements.
-
Automate Triggering of Load Tests:
Typically, load tests are run after significant changes are made to the application, such as after merging a feature into the main branch. You can automate this by adding a step to your CI pipeline that triggers a LoadForge test. This can usually be done through LoadForge's API.
Example CLI command to trigger a LoadForge test:
curl -X POST "https://api.loadforge.com/tests/your-test-id/start" \
-H "Authorization: Token your_api_token" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json"
-
Analyze and Feedback:
Upon completion of the test, gather results and metrics from LoadForge which you can then review to identify performance bottlenecks or regressions introduced by the latest changes. Incorporate these insights into your development process for necessary adjustments.
-
Alerting:
Configure alerts in LoadForge to notify the team when the performance thresholds go beyond acceptable limits. This informs the immediate review and potential rollback of problematic changes.
Benefits of Continuous Load Testing
Regularly integrating load testing into your development and deployment cycle offers several advantages:
- Early Detection of Performance Issues: Catching and resolving problems early in the development stage reduces the risk of deploying a poor-performing update to production.
- Consistent Performance Assurance: Regular testing helps maintain consistent standards of site performance as new updates are continually integrated.
- Data-Driven Performance Optimization: Ongoing tests generate a wealth of data that can be used to make informed decisions about optimizations and improvements.
Challenges and Considerations
While integrating regular load testing into your CI/CD process is highly beneficial, here are a few challenges and considerations to keep in mind:
- Resource Allocation: Ensure that you have adequate resources (servers, bandwidth, etc.) dedicated to running these tests especially for large-scale tests.
- Test Maintenance: Keep your testing scenarios updated with new website features and changes to maintain relevance and effectiveness of the tests.
- Balancing Frequency and Overhead: Decide on a reasonable balance between the frequency of tests and the resource load they place on your CI/CD systems.
By embedding LoadForge load tests into your CI/CD process, your Drupal site can achieve not just initial excellence but sustained quality and reliability. This proactive approach to performance testing ensures your Drupal site remains equipped to deliver superior user experiences, irrespective of the scale or change it undergoes.