Introduction to Load Testing Laravel Applications
In the fast-paced world of web development, ensuring that your applications can handle expected traffic levels and maintain performance under stress is not just an advantage—it’s a necessity. Laravel, a popular PHP framework, is known for its elegant syntax and robust features that accommodate the needs of all kinds of web applications. However, as these applications expand and user bases grow, their vulnerability to performance issues increases. This emphasizes the need for thorough load testing.
Load testing involves simulating real-life load conditions on your application to verify its performance and stability. This testing is crucial for identifying bottlenecks and areas of improvement in your application before they affect your end users. For Laravel applications, which are often dynamic and contain multiple dependencies, specialized testing ensures that both the application and its infrastructure are scalable and robust.
Why is Load Testing Essential for Laravel Applications?
By load testing your Laravel application, you are essentially preparing it to perform smoothly under high traffic conditions. Here are a few reasons why load testing is pivotal:
- Scalability Testing: Load testing helps in understanding how well your Laravel application can scale up during peak traffic times. This is crucial for planning capacity additions and infrastructure scaling.
- Robustness: It tests the durability and stability of your Laravel application under stressful conditions, ensuring that your application won’t crash or lose data when it matters most.
- Performance Optimization: Through load testing, developers can identify which parts of the Laravel application are slowing down under load. This allows for targeted optimizations, improving overall application responsiveness and user experience.
- Cost Management: Efficiently predicting and managing the load can help in cost optimizations of server resources and services, avoiding over-spending on under-utilized resources.
Basic Concepts of Load Testing
Load testing your Laravel application involves several key concepts:
- Virtual Users (VUs): These are simulated users that interact with your application during the test, performing tasks that real users would do.
- Response Time: This measures how long it takes for the server to respond to a user request, which is a critical indicator of your application's performance.
- Throughput: This is the number of requests that can be handled by your application at any given time.
- Resource Utilization: Tracks how much CPU, memory, and network resources are consumed during the test.
Understanding these metrics provides insights into how changes to your application or its environment affect its ability to handle real-world scenarios.
Laravel-Specific Load Testing
Laravel applications often utilize unique features such as job queues, event broadcasting, and various caching mechanisms, making generic testing insufficient. Tailored load tests consider these specifics:
- Middleware Performance: Laravel uses middleware for handling HTTP requests efficiently. Testing how middleware behaves under load can point to necessary optimizations.
- Eloquent Relationships: Laravel's Eloquent ORM is easy to use but can become a performance drag if not optimized for heavy loads. Testing helps highlight inefficient database queries.
- Route Performance: Since routes are the entry point of all requests in a Laravel application, load testing helps in optimizing these critical paths for faster response times.
Effectively load testing Laravel applications not only ensures a seamless user experience but also helps in maintaining the reliability and integrity of your application. As we move forward in this guide, we will delve into preparing your environment, crafting a basic but effective Locustfile, and eventually running and analyzing your tests using LoadForge, ensuring that your Laravel application meets the rigorous demands of the real world.
Preparing Your Laravel Environment
When preparing your Laravel application for load testing, it is crucial to ensure that the environment is properly set up to simulate a realistic user experience under various load conditions. This preparation involves configuring your development, staging, and production environments appropriately, as well as optimizing your Laravel application to handle the tests effectively. Below, we outline the steps to prepare your Laravel environment for load testing.
1. Environment Configuration
Before beginning load testing, ensure that your Laravel environments (development, staging, and production) are aligned with the actual usage conditions expected in production. This often involves the following steps:
-
Development Environment: Typically used by developers for building and initial testing. It should mimic the production environment as closely as possible, although performance optimizations might not be fully implemented.
-
Staging Environment: Serves as a pre-production area where all elements of the application are tested together. This environment should be a clone of the production setup, including database, server configurations, and third-party integrations.
-
Production Environment: The live environment where your application is accessed by real users. This environment should have all the performance optimizations in place.
2. Application Optimization
Optimizing your Laravel application before load testing is essential to avoid misleading results caused by inefficiencies in the code or configuration. Consider the following optimizations:
-
Database Tuning: Optimize queries, use indexing, and consider caching results to reduce the load on your database. Laravel's Eloquent ORM can be tuned using proper indexing and eager loading of relationships to minimize the number of queries on each request.
-
Caching: Implement caching mechanisms to reduce the load on your database and speed up request processing. Laravel supports several caching backends like Memcached and Redis out of the box.
-
Configuration Caching: Use Laravel's configuration caching feature to combine all configuration files into a single, optimized file that loads faster.
php artisan config:cache
-
Route Caching: If your application has a large number of routes, consider using route caching to reduce the computation of routes on each request.
php artisan route:cache
-
Asset Optimization: Minimize and combine CSS and JavaScript files and use Laravel Mix to compile assets efficiently.
3. Environment Specific Configuration
Ensure that your .env files for each environment are configured correctly to reflect the individual characteristics of each environment, such as database connections, mail drivers, and other third-party services. Keep your production environment variables secure.
4. Monitoring and Logging
Implement monitoring and logging tools to keep track of your application's performance and to identify potential issues quickly. Laravel offers integration with various logging services that can be configured to handle logs appropriately based on the environment.
5. Testing Data
Prepare your database with sufficient data to mimic real-world usage. Use Laravel's seeders and factories to populate the database with test data.
php artisan db:seed
Conclusion
By following these steps, your Laravel application will be well-prepared for effective load testing. Ensuring that each environment is configured correctly and the application is optimized for performance allows for the most accurate and reliable load testing outcomes.
Writing a Basic Locustfile
This section will guide you through the creation of a basic Locustfile. A Locustfile is a Python script used for defining user behavior and simulating traffic against your web application, in this case, a Laravel application. We’ll start with how to set up user behaviors, simulate user tasks, and configure the file specifically for load testing your Laravel environment.
Setting Up Your Environment
To start, make sure you have Python and Locust installed. You can install Locust using pip:
pip install locust
Create a new Python file named locustfile.py in your project directory. This file will contain the load testing script for your Laravel application.
Defining User Behavior
In Locust, users are simulated using classes that inherit from User. Each class can define the behavior of users through tasks defined as methods. Below is the structure of a basic user class:
from locust import HttpUser, task, between
class LaravelUser(HttpUser):
host = "https://your-laravel-site.com"
wait_time = between(1, 5) # Simulate real-user wait time between task execution
@task
def load_homepage(self):
self.client.get("/")
In this example:
LaravelUser is a user class representing a user of your Laravel application.host is the base URL of your Laravel application.wait_time defines the average time between the task executions to mimic real user interaction.@task decorator is used to define a task. In this case, load_homepage is a task that hits the homepage of your Laravel site.
Simulating User Tasks
To replicate user interaction with various endpoints of your Laravel application, you can add more methods to LaravelUser. Here’s an example that includes additional tasks:
@task(2)
def view_posts(self):
self.client.get("/posts")
@task(1)
def submit_form(self):
self.client.post("/submit", data={"name": "test", "email": "test@example.com"})
Tasks can have different weights (@task(2)), signifying the likelihood of the task being executed relative to others. In this example, the view_posts task is twice as likely to be executed as submit_form.
Configuring Request Headers and Managing Sessions
To handle sessions or add specific headers required by your Laravel application (like CSRF tokens), customize the HTTP client through the on_start method. This is executed when a simulated user starts:
def on_start(self):
response = self.client.get("/login")
csrftoken = response.cookies['XSRF-TOKEN']
self.client.headers.update({"X-CSRF-TOKEN": csrftoken})
This function fetches a CSRF token from a Laravel login form and updates the session headers for subsequent requests.
Conclusion
This basic setup offers a streamlined introduction to using Locust for load testing a Laravel application. You've established user behavior, created tasks to simulate web actions, and configured essential elements like headers and sessions.
Next, you'll enhance your Locustfile for more complex scenarios in the following sections, building upon this foundational knowledge to apply more extensive testing strategies to your Laravel application.
Enhancing Your Locustfile for Complex Scenarios
In this section, we delve into expanding the basic Locustfile to handle more complex testing scenarios for your Laravel application. We aim to simulate heavy user loads, test specific API endpoints effectively, and manage the complexities of concurrent users performing diverse tasks. By enhancing your Locustfile, you can ensure a more comprehensive understanding of how your application behaves under various stress conditions.
Simulating Heavy User Load
To test how your Laravel application handles heavy user traffic, you will need to increase the number of simulated users and adjust the spawn rate accordingly. Here’s how you can modify your Locustfile to simulate this scenario:
from locust import HttpUser, task, between
class HeavyLoadUser(HttpUser):
wait_time = between(1, 3) # Users will wait 1-3 seconds between tasks
@task(10)
def view_homepage(self):
self.client.get("/")
@task(20)
def perform_task(self):
with self.client.post("/task", json={"task": "value"}, catch_response=True) as response:
if response.status_code != 200:
response.failure("Failed to perform task")
In the above example, @task(10) and @task(20) depict the different weights, indicating how often each task is executed. By increasing these numbers, you create a heavier load profile.
Testing API Endpoints
Testing API endpoints requires specific focus on the requests being sent and how the application processes them. Here’s a modified Locustfile snippet to test several API endpoints:
from locust import HttpUser, task, between
class ApiUser(HttpUser):
wait_time = between(2, 5)
@task
def get_users(self):
self.client.get("/api/users")
@task
def add_user(self):
self.client.post("/api/users", json={"name": "John Doe", "email": "john@example.com"})
This configuration tests both GET and POST requests to your application’s user-related API endpoints.
Managing Concurrent Users Performing Diverse Tasks
In real-world scenarios, different users might be performing different actions on your application. Here’s a way to simulate this:
from locust import HttpUser, task, between, TaskSet
class UserBehavior(TaskSet):
@task(2)
def page_one(self):
self.client.get("/page1")
@task(1)
def page_two(self):
self.client.get("/page2")
class WebsiteUser(HttpUser):
tasks = [UserBehavior]
wait_time = between(5, 9)
This setup uses a TaskSet to group tasks that can be assigned different weights, thus simulating users browsing different parts of your site at varying frequencies.
Configuration Recommendations
When enhancing your Locustfile for complex scenarios, consider the following configuration tips:
- Increase the Hatch Rate: A higher hatch rate allows more users to spawn simultaneously, which is useful for testing how your application handles spike loads.
- Utilize On-Start Tasks: Define tasks that run when a Locust user starts, which can include setup operations like logging in users before performing further actions.
- Implement Task Sequences: If you need to simulate a sequence of actions (e.g., user logs in, performs a task, logs out), look into using
SequentialTaskSet for a more realistic user flow.
By enhancing your Locustfile as discussed, you not only test the resilience of your Laravel application under heavy loads and complex user interactions but also get detailed insights into specific areas that might need optimization.
Running Your Test with LoadForge
After creating and configuring your Locustfile for a Laravel application, the next step is to run the test using the LoadForge platform. This section will guide you through the process of setting up and executing your load test on LoadForge, including how to configure user numbers, spawn rates, and leverage geo-distribution features to simulate traffic from various global locations.
Step 1: Uploading Your Locustfile to LoadForge
LoadForge allows you to upload your Locustfile directly to the platform, making it easy to manage and execute load tests:
- Log into your LoadForge account.
- Navigate to the Scripts section on the dashboard.
- Click on Create New Script.
- Provide a name for your script and choose Locust as the script type.
- Upload your Locustfile or copy and paste the script into the provided text area.
- Click Save to store your script on the platform.
Step 2: Configuring Test Parameters
With your script uploaded, the next stage involves setting specific parameters for how the test should run:
- Navigate to the Tests section and click New Test.
- Select the script you uploaded from the drop-down menu.
- Configure the Test Settings:
- Duration: Set how long the test should run.
- Users: Specify the number of concurrent users LoadForge should simulate.
- Spawn Rate: Define the rate at which new users are spawned per second.
Sample Configuration
Here's an example of test parameter settings you might use:
Duration: 10 minutes
Users: 1000
Spawn Rate: 50 users per second
Step 3: Using Geo-Distribution Features
To realistically simulate how your application handles traffic from different geographical locations, LoadForge offers geo-distribution capabilities:
- In the Test Settings, find the Geo-Distribution section.
- Check the Enable Geo-Distribution box.
- Select the locations from which you want to simulate users. Options typically include various countries and regions around the world.
- Adjust the percentage of traffic to simulate from each location if needed.
Step 4: Running the Test
Once all configurations are set:
- Review your settings to ensure everything is correctly configured.
- Click Start Test to initiate the load test.
- Monitor the test in real-time through the LoadForge dashboard, which provides insights into response times, request rates, and errors.
Step 5: Stopping the Test
If you need to stop the test at any point due to unexpected issues or if you've gathered enough data:
- Go to the active test view.
- Click Stop Test to halt all testing actions immediately.
Conclusion
Running your Laravel application load test through LoadForge is straightforward once you have your Locustfile in place. By properly configuring test parameters and utilizing the platform's geo-distribution capabilities, you can obtain valuable insights into how well your application performs under stress from various global points. This testing process helps ensure that your Laravel application can scale and maintain robustness irrespective of user demand.
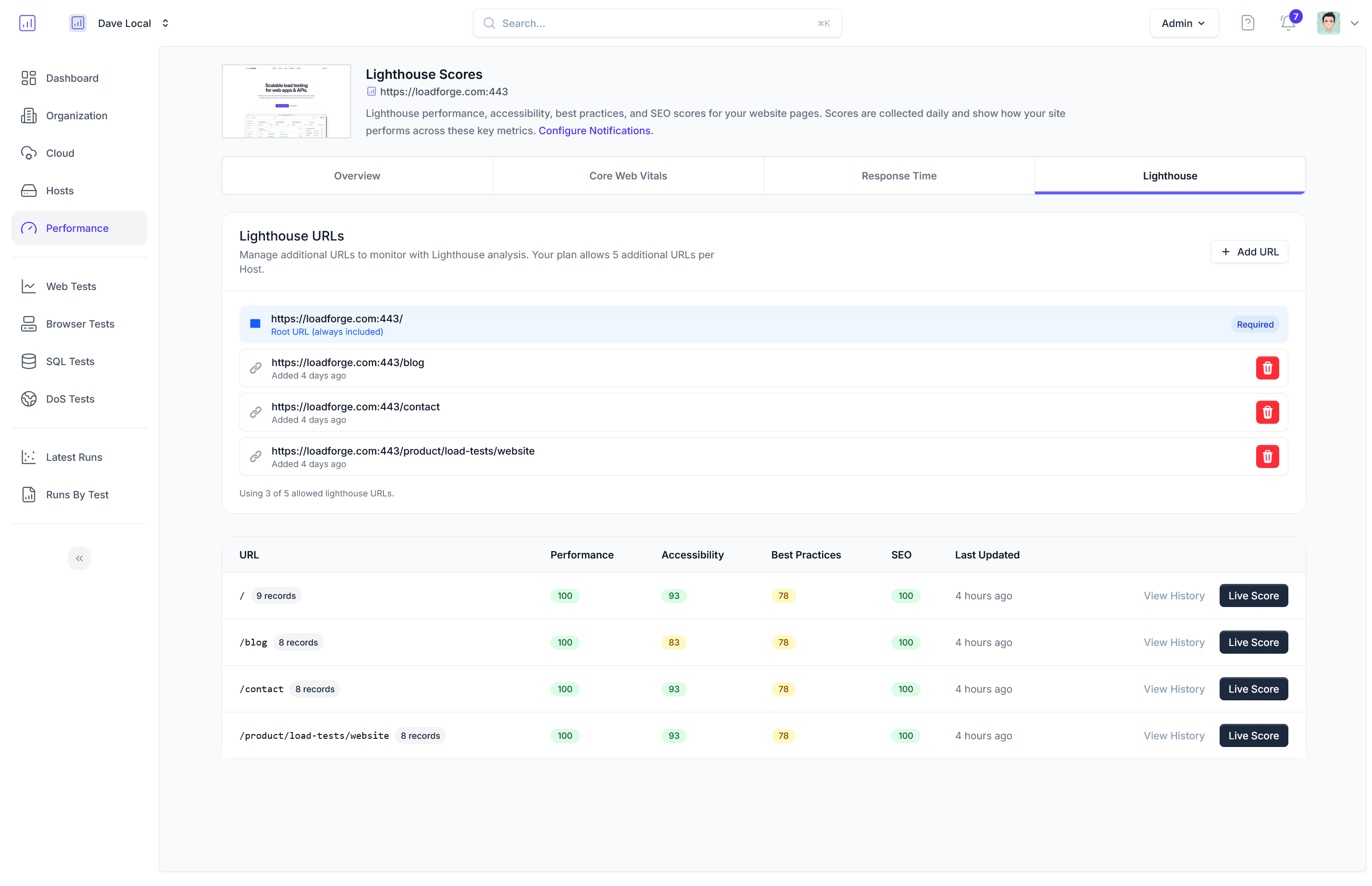
Analyzing the Results
After conducting a thorough load test on your Laravel application using LoadForge, the next critical step involves analyzing the generated results. This evaluation is essential to grasp the resilience and efficiency of your application under various load conditions. In this section, we will explore how to interpret the results provided by LoadForge, identify potential bottlenecks, and make informed decisions to enhance your application's performance.
Understanding LoadForge Results
When a test concludes, LoadForge offers a detailed report encapsulating several key metrics. These include:
- Requests Per Second (RPS): Measures the number of requests your application can handle each second. A higher RPS indicates better performance under load.
- Response Times: Tracks the minimum, maximum, and average response times. Longer response times can indicate performance issues.
- Error Rates: Displays the percentage of failed requests. High error rates may suggest stability problems or insufficient resources.
- User Load: Shows how the application performs as the number of concurrent users increases.
A typical section of the LoadForge result might look like this:
{
"total_rps": 450.0,
"avg_response_time": 150,
"min_response_time": 100,
"max_response_time": 300,
"error_rate": 0.05,
"user_load": 200
}
Identifying Bottlenecks
With the data from LoadForge, you can pinpoint various bottlenecks that could be affecting your application:
- High Response Times: Review endpoints or functions that show longer response times. Check if optimizations such as database indexing, query optimization, or caching might be necessary.
- Increased Error Rate: An increase in errors under higher loads often points to limits being reached, such as database connections or server resources.
- Resource Utilization: Monitor server metrics (CPU usage, memory usage) during tests to see if hardware constraints are a bottleneck.
Making Data-Driven Decisions
Analyzing the load test results enables you to make targeted improvements:
- Optimizing Code and Queries: Refactor slow-running functions or database queries highlighted by the test.
- Scaling Resources: If resource limits are reached (e.g., CPU, memory), consider scaling up your server or using load balancing solutions.
- Improving Stability: Address areas with high error rates by increasing timeout settings, upgrading server capabilities, or revising error handling logic.
Visualizing the Data
For a more intuitive analysis, visualize the results using LoadForge's built-in graphs or by exporting the data for use in tools like Grafana or Google Sheets. Here’s how you might set up a simple visualization:
Plot 'Users' on X-axis and 'Average Response Time' on Y-axis to see how response time varies with user load.
Conclusion
Effectively analyzing the results from your load tests allows you to fine-tune your Laravel application, ensuring it can withstand the demands of real-world usage. By following a methodical approach to interpreting LoadForge data, identifying critical bottlenecks, and implementing improvements, you can significantly enhance the performance and reliability of your application.
Best Practices for Ongoing Laravel Load Testing
Successful load testing is not a one-and-done event—it's a continuous part of a healthy development lifecycle. Integrating routine load testing into your process improves the reliability and performance of your Laravel applications. Here are some essential best practices you should adopt to maximize the benefits of ongoing load testing.
Implement Routine Load Testing
Routine load testing should be integrated into your regular development schedule. This ensures that any performance degradations or scalability issues are caught and addressed early.
- Schedule Regular Tests: Define a schedule for your load tests—weekly, biweekly, or another interval that fits your development cycle.
- Automate Tests: Use CI/CD tools to automate load testing. This can be done by setting up hooks that trigger a load test after major commits or during off-peak hours.
Example CI/CD config snippet to automate Locust tests:
jobs:
load_test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Run Locust
run: locust -f locustfile.py --headless -u 100 -r 10
Monitor Improvements Over Time
To effectively improve the performance of your application, tracking the results of each test over time is crucial. This data will help you understand how changes in your codebase affect performance.
- Use a Performance Dashboard: Tools like LoadForge offer dashboards that can help visualize test results, making it easier to compare data over time.
- Set Performance Benchmarks: Establish performance goals for your application and use them as benchmarks to measure against after each load test.
Adjust Tests Based on Insights
As you gather data from your load tests, you'll begin to identify patterns and bottlenecks. Utilize these insights to adapt and evolve your testing strategies.
- Refine Test Scenarios: Based on test results, modify your Locustfiles to better simulate user behavior or to stress-test newly identified weak points.
- Scale Tests with Application Growth: As your user base grows, scale your testing parameters to simulate loads that your application is more likely to encounter in the real world.
Encourage a Culture of Performance Awareness
Make load testing and performance optimization a regular topic of discussion among your development team.
- Review Test Results Regularly: Hold regular meetings to review test results and discuss necessary improvements or changes in the development approach.
- Educate Your Team: Ensure all team members understand the importance of performance and are trained in using tools like LoadForge for monitoring and analyzing test results.
Continuously Update Testing Tools and Strategies
As technologies evolve, so should your testing tools and methods to ensure they remain effective.
- Stay Updated with LoadForge Releases: Regularly update the LoadForge tool and any dependent libraries to leverage new features and improvements.
- Explore New Testing Techniques: Keep abreast of the latest in load testing methodologies and tools. Experiment with new features and integrate them if they offer improvements.
By following these best practices, you ensure that load testing becomes an integral and effective part of your development process, not just a checkbox in project management. This ongoing cycle of testing, monitoring, and adjusting stages develops a robust, scalable Laravel application that can handle the demands of real-world use with confidence.