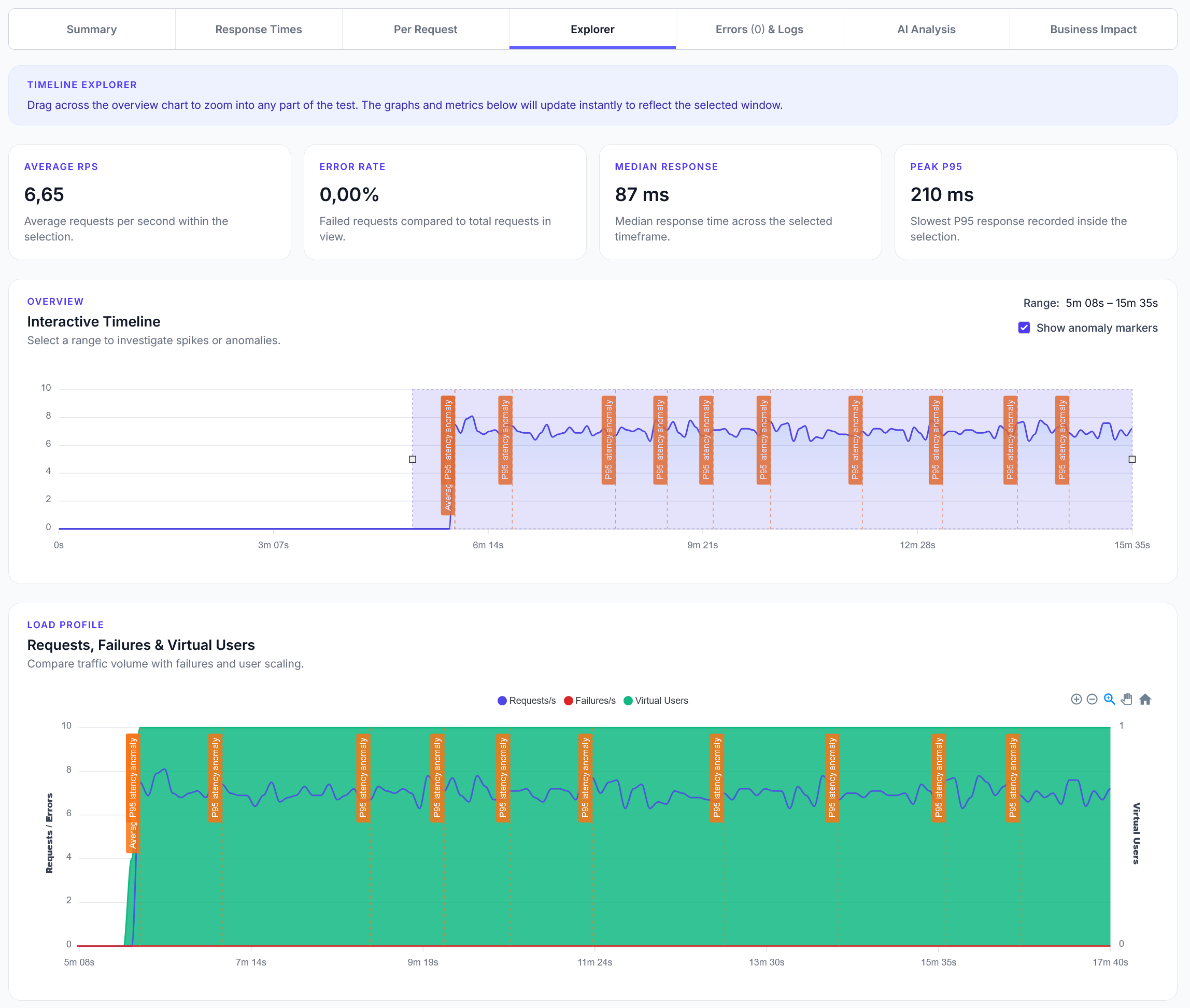
Explorer reports addition
We have added a new Explorer feature to reports, with a timeline scrubber and easy anomaly detection.
Guide on load testing WebSocket-based applications with LoadForge using Locust.
LoadForge can record your browser, graphically build tests, scan your site with a wizard and more. Sign up now to run your first test.
LoadForge provides support for generic WebSocket testing via the WebSocketUser from locust-plugins. You can open WebSocket connections, send and receive messages, and simulate concurrency to measure performance under load.
# locust.py
import time
from locust import HttpUser, between, task
from locust_plugins.users import WebSocketUser
class MyWebSocketUser(WebSocketUser):
wait_time = between(1, 3)
host = "wss://YOUR_WS_URL_HERE"
def on_start(self):
# Connect to WebSocket server
self.connect("/ws")
@task
def send_message(self):
# Send a message to the WebSocket
self.send("hello", name="SendMessage")
# Optionally wait for server response
time.sleep(1)
def on_message(self, message):
# Handle incoming message
print(f"Received: {message}")
Notes:
pip install locust locust-plugins websockets if you wish to test locally.YOUR_WS_URL_HERE and endpoint /ws with your actual WebSocket URL and path.