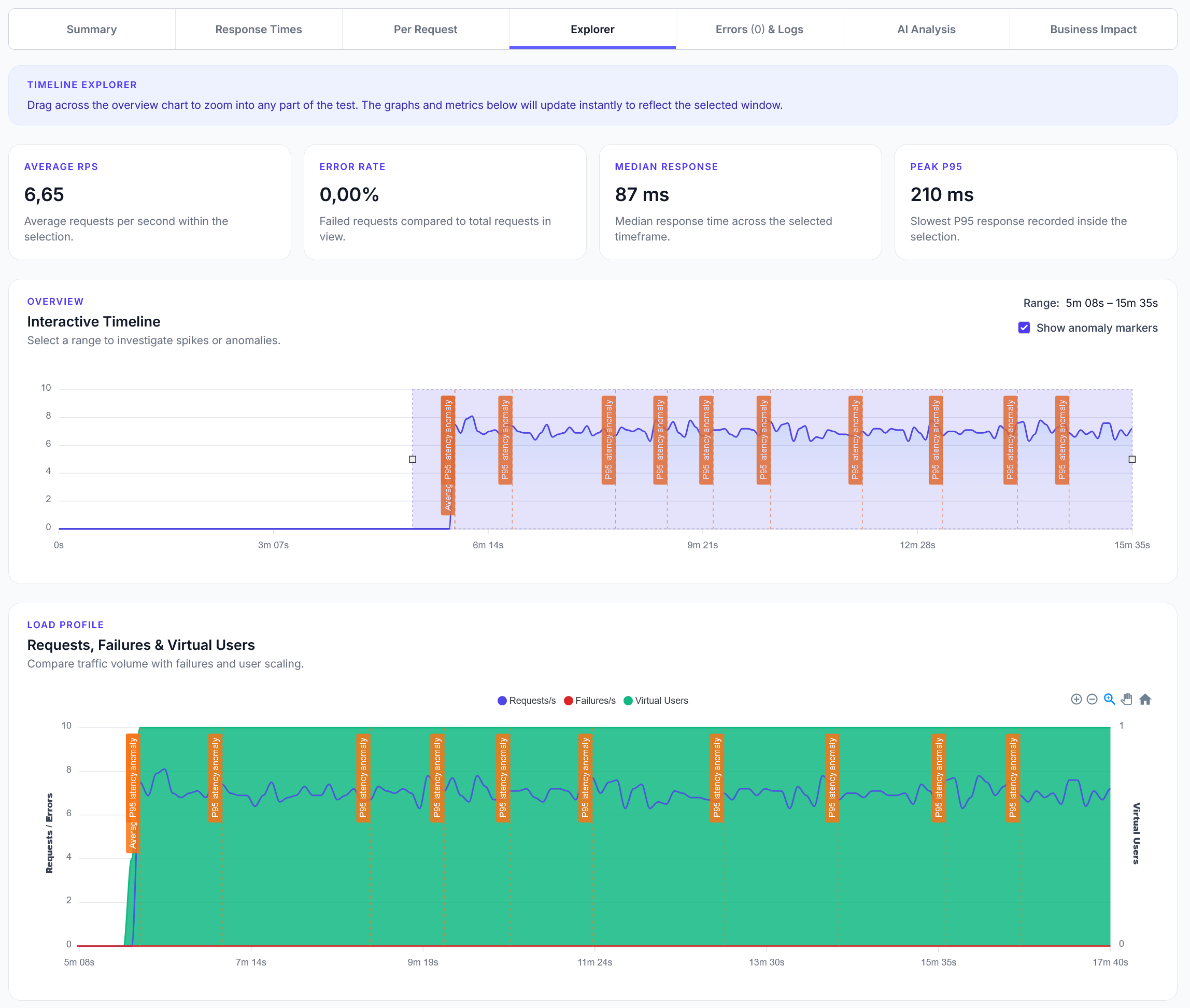
Explorer reports addition
We have added a new Explorer feature to reports, with a timeline scrubber and easy anomaly detection.
Complete OAuth 2.0 authorization code flow with PKCE (Proof Key for Code Exchange) for secure authentication testing
LoadForge can record your browser, graphically build tests, scan your site with a wizard and more. Sign up now to run your first test.
This locustfile demonstrates how to test a complete OAuth 2.0 authorization code flow with PKCE (Proof Key for Code Exchange). This is commonly used by modern web applications and SPAs for secure authentication.
import base64
import hashlib
import secrets
import urllib.parse
from locust import HttpUser, task, between
import json
import re
class OAuth2User(HttpUser):
wait_time = between(1, 3)
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
# OAuth 2.0 Configuration - Update these for your provider
self.client_id = "your-client-id"
self.redirect_uri = "https://your-app.com/callback"
self.auth_server = "https://your-auth-server.com"
self.scope = "openid profile email"
# PKCE parameters
self.code_verifier = None
self.code_challenge = None
self.state = None
self.authorization_code = None
self.access_token = None
self.refresh_token = None
def generate_pkce_parameters(self):
"""Generate PKCE code verifier and challenge"""
# Generate code verifier (43-128 characters)
self.code_verifier = base64.urlsafe_b64encode(
secrets.token_bytes(32)
).decode('utf-8').rstrip('=')
# Generate code challenge
challenge_bytes = hashlib.sha256(self.code_verifier.encode('utf-8')).digest()
self.code_challenge = base64.urlsafe_b64encode(challenge_bytes).decode('utf-8').rstrip('=')
# Generate state parameter
self.state = secrets.token_urlsafe(32)
def on_start(self):
"""Initialize OAuth flow when user starts"""
self.generate_pkce_parameters()
self.initiate_oauth_flow()
def initiate_oauth_flow(self):
"""Step 1: Initiate OAuth 2.0 authorization request"""
auth_params = {
'response_type': 'code',
'client_id': self.client_id,
'redirect_uri': self.redirect_uri,
'scope': self.scope,
'state': self.state,
'code_challenge': self.code_challenge,
'code_challenge_method': 'S256'
}
auth_url = f"{self.auth_server}/oauth/authorize?" + urllib.parse.urlencode(auth_params)
with self.client.get(
auth_url,
name="OAuth: Authorization Request",
catch_response=True,
allow_redirects=False
) as response:
if response.status_code in [200, 302]:
response.success()
# In a real scenario, user would login here
# For testing, we simulate getting the authorization code
self.simulate_user_login()
else:
response.failure(f"Authorization request failed: {response.status_code}")
def simulate_user_login(self):
"""Step 2: Simulate user login and consent"""
# This simulates the user login form submission
login_data = {
'username': 'test@example.com',
'password': 'testpassword',
'state': self.state
}
with self.client.post(
f"{self.auth_server}/oauth/login",
data=login_data,
name="OAuth: User Login",
catch_response=True,
allow_redirects=False
) as response:
if response.status_code in [200, 302]:
response.success()
# Extract authorization code from redirect
if 'Location' in response.headers:
location = response.headers['Location']
self.extract_authorization_code(location)
else:
# Sometimes the code is in the response body
self.extract_authorization_code_from_body(response.text)
else:
response.failure(f"User login failed: {response.status_code}")
def extract_authorization_code(self, redirect_url):
"""Extract authorization code from redirect URL"""
parsed_url = urllib.parse.urlparse(redirect_url)
query_params = urllib.parse.parse_qs(parsed_url.query)
if 'code' in query_params:
self.authorization_code = query_params['code'][0]
# Verify state parameter
if 'state' in query_params and query_params['state'][0] == self.state:
self.exchange_code_for_tokens()
else:
print("State parameter mismatch - potential CSRF attack")
else:
print("No authorization code received")
def extract_authorization_code_from_body(self, response_body):
"""Extract authorization code from response body (alternative method)"""
# Look for authorization code in response body
code_match = re.search(r'code=([^&\s]+)', response_body)
if code_match:
self.authorization_code = code_match.group(1)
self.exchange_code_for_tokens()
def exchange_code_for_tokens(self):
"""Step 3: Exchange authorization code for access token"""
if not self.authorization_code:
return
token_data = {
'grant_type': 'authorization_code',
'client_id': self.client_id,
'code': self.authorization_code,
'redirect_uri': self.redirect_uri,
'code_verifier': self.code_verifier
}
with self.client.post(
f"{self.auth_server}/oauth/token",
data=token_data,
name="OAuth: Token Exchange",
catch_response=True
) as response:
if response.status_code == 200:
response.success()
token_response = response.json()
self.access_token = token_response.get('access_token')
self.refresh_token = token_response.get('refresh_token')
print(f"Successfully obtained access token")
else:
response.failure(f"Token exchange failed: {response.status_code}")
@task(3)
def make_authenticated_request(self):
"""Make authenticated API requests using the access token"""
if not self.access_token:
return
headers = {
'Authorization': f'Bearer {self.access_token}',
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
}
with self.client.get(
"/api/user/profile",
headers=headers,
name="API: Authenticated Request",
catch_response=True
) as response:
if response.status_code == 200:
response.success()
elif response.status_code == 401:
# Token might be expired, try to refresh
response.failure("Access token expired")
self.refresh_access_token()
else:
response.failure(f"Authenticated request failed: {response.status_code}")
@task(1)
def refresh_access_token(self):
"""Step 4: Refresh access token using refresh token"""
if not self.refresh_token:
return
refresh_data = {
'grant_type': 'refresh_token',
'client_id': self.client_id,
'refresh_token': self.refresh_token
}
with self.client.post(
f"{self.auth_server}/oauth/token",
data=refresh_data,
name="OAuth: Token Refresh",
catch_response=True
) as response:
if response.status_code == 200:
response.success()
token_response = response.json()
self.access_token = token_response.get('access_token')
# Some providers issue new refresh tokens
if 'refresh_token' in token_response:
self.refresh_token = token_response['refresh_token']
print("Successfully refreshed access token")
else:
response.failure(f"Token refresh failed: {response.status_code}")
@task(1)
def revoke_token(self):
"""Optional: Revoke tokens (logout)"""
if not self.access_token:
return
revoke_data = {
'token': self.access_token,
'client_id': self.client_id
}
with self.client.post(
f"{self.auth_server}/oauth/revoke",
data=revoke_data,
name="OAuth: Token Revocation",
catch_response=True
) as response:
if response.status_code in [200, 204]:
response.success()
self.access_token = None
self.refresh_token = None
print("Successfully revoked tokens")
else:
response.failure(f"Token revocation failed: {response.status_code}")
Before running this test in LoadForge, update these variables:
# OAuth 2.0 Provider Configuration
self.client_id = "your-oauth-client-id"
self.redirect_uri = "https://your-app.com/callback"
self.auth_server = "https://your-auth-provider.com"
self.scope = "openid profile email" # Adjust scopes as needed
This pattern works with:
https://your-domain.auth0.comhttps://your-domain.okta.comhttps://accounts.google.comhttps://login.microsoftonline.comhttps://github.com/login/oauthclient_id configurationWhen you add this test to LoadForge, you'll be able to see detailed metrics on each step of the OAuth flow, helping you identify bottlenecks in your authentication system.