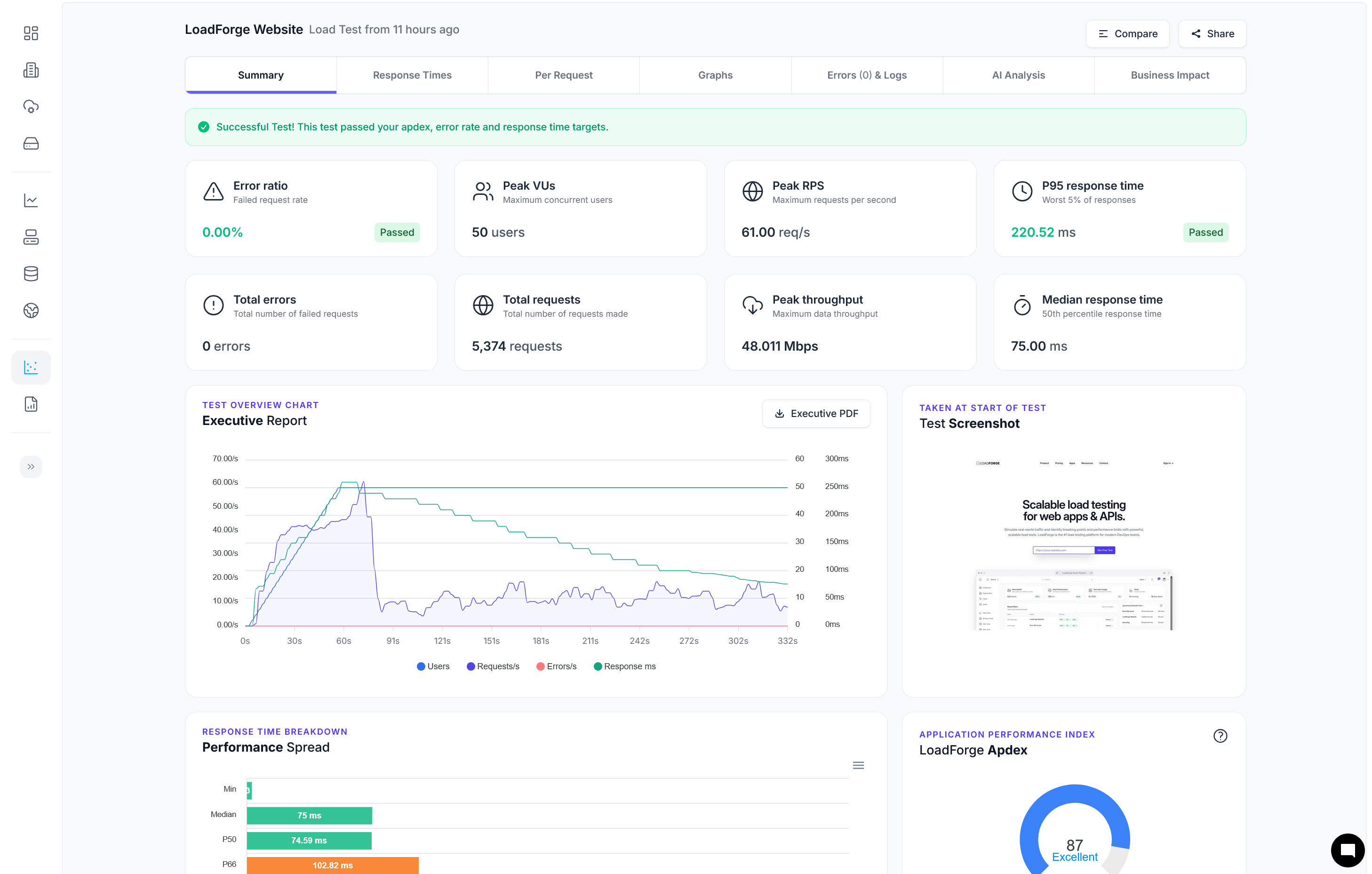
mysqldumpslow -t 10 /path/to/your/slow-query.log
This command outputs the top 10 queries that appear most frequently in your slow query log. Using options like `-s at` can sort the output by average query time, helping you focus on the most time-consuming queries.
### Practical Analysis Tips
- **Focus on Queries with High Frequency**: A query that appears frequently and has a high execution time can have a cumulative negative impact on performance.
- **Look for Patterns**: Are there specific times of day when slow queries occur? Are specific database tables consistently involved in slow queries?
- Republicantas from your analyses to team discussions and development sprints to ensure everyone understands database performance implications.
- **Regular Reviews**: Make analyzing slow query logs a regular part of your database maintenance routine to continually refine and optimize query performance.
By learning how to effectively analyze slow query logs, you can proactively manage and enhance the performance of your MySQL database, leading to faster response times and a more efficient application overall.
## Tools for Analyzing Slow Query Logs
To efficiently analyze the data captured in MySQL slow query logs, leveraging the right set of tools is crucial. These tools interpret, simplify, and visualize the complexities of log files, making it easier to pinpoint performance bottlenecks. In this section, we explore a variety of tools ranging from simple command-line utilities to more comprehensive monitoring systems that can aid in the effective analysis of slow query logs.
### 1. **Percona Toolkit**
Percona Toolkit is a collection of advanced command-line tools that assist in the performance optimization of MySQL databases. Among these tools, `pt-query-digest` is particularly useful for analyzing MySQL slow query logs. It provides a detailed report of query execution time, helping you to focus on the queries that require the most attention.
**Usage Example:**
pt-query-digest /path/to/your/slow-query.log
This command parses the slow query log file and outputs a summary of the most time-consuming queries. It's a great starting point to identify which queries need optimization.
2. MySQL Workbench
MySQL Workcluster, the official GUI for managing MySQL databases, includes a suite of performance diagnosis tools. The Performance Reports feature can import slow query logs and provide graphical representations of execution times and other critical metrics.
Features:
- Visualization of query performance.
- Filters to isolate specific queries.
- Direct access to query optimization tools.
3. EverSQL
EverSQL is a software service that not only helps in analyzing slow query logs but also provides recommendations for speeding up SQL queries automatically. By uploading your slow query log to EverSQL, it uses AI to generate suggestions for indexes and query rewrites.
Benefits:
- Query optimization suggestions based on actual log data.
- Easy integration with existing SQL workflows.
- Tracks and compares performance improvements.
4. Logstash
If you're processing logs centrally, including slow query logs, Logstash from the Elastic Stack can be configured to parse and visualize these logs. With its powerful filter plugins, such as the grok parser, you can extract structured data from the complex log entries.
Logstash Filter Example:
filter {
grok {
match => { "message" => "%{GREEDYDATA:mysql_error}" }
}
}
This configuration helps in transforming the slow query logs into structured data, which can be further analyzed using Elasticsearch and visualized with Kibana.
5. Zabbix
Zabbix is an enterprise-grade open-source monitoring software. It can be configured to monitor MySQL performance, including the analysis and alerting based on slow query logs. Zabbix can use triggers to alert the administrator when the number of slow queries exceeds a threshold, which ensures proactive performance management.
Key Features:
- Real-time monitoring.
- Customizable alerts.
- Comprehensive reports and dashboards.
Conclusion
Choosing the right tool or combination of tools depends largely on your specific needs, the complexity of your environment, and the level of detail you require from your analyses. Whether you prefer a command-line approach with pt-query-digest or a more graphical interface with MySQL Workbench, these tools can significantly enhance your ability to analyze slow query logs effectively and improve your database performance.
Optimizing Queries
Once you have identified slow queries using MySQL Slow Query Logs, the next essential step is to optimize those queries to enhance your database's performance. This section provides guidance on refining your SQL queries to ensure they are both efficient and effective. Here, we will explore various strategies and tips for writing optimal SQL commands.
1. Indexing
Indexing is one of the most powerful tools at your disposal for query optimization. Properly indexed tables can dramatically decrease the amount of time it takes to execute queries.
- Use the EXPLAIN statement: Before indexing, use the
EXPLAIN statement to understand how MySQL executes your query and which indexes might be beneficial.
- Index Columns Used in WHERE Clauses: Adding indexes to columns used frequently in WHERE clauses can help speed up data retrieval by reducing the number of rows the database engine needs to scan.
ALTER TABLE your_table_name ADD INDEX (column_name);
2. Optimizing Joins
Poorly designed joins can degrade performance significantly, especially with large datasets.
- Limit the number of rows in a JOIN: Use the
ON clause to limit the results as early as possible in the execution plan.
- Prefer INNER JOIN over OUTER JOIN: INNER JOINS are generally faster than OUTER JOINS if you don’t need the full outer results.
SELECT a.name, b.price
FROM products a
INNER JOIN sales b ON a.id = b.product_id
WHERE a.stock > 0;
3. Query Refactoring
Refining the structure of your SQL query can lead to significant improvements in performance.
- **Avoid SELECT ***: Specify only the columns you need rather than using
SELECT * to reduce the data load.
- Reduce Subqueries: Flatten subqueries where possible, converting them to joins or temporary tables to minimize complexity.
SELECT name, price FROM products WHERE id IN (SELECT product_id FROM sales);
4. Using Temporary Tables
For complex queries, especially those involving multiple joins or subqueries, using temporary tables can help by breaking down the query into simpler steps.
- Create temporary tables to simplify queries: Store the intermediate results in a temporary table to avoid repeated complex calculations.
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE temp_products
SELECT product_id, SUM(sales) as total_sales
FROM sales
GROUP BY product_id;
SELECT a.name, b.total_sales
FROM products a
JOIN temp_products b ON a.id = b.product_id;
5. Proper Use of Aggregate Functions
Aggregations can be resource-intensive. Optimizing their use is crucial for improving query performance.
- Filter before aggregating: Apply WHERE clauses before aggregations to minimize the number of rows being aggregated.
SELECT category, COUNT(*) as total_products
FROM products
WHERE price > 100
GROUP BY category;
6. Parameter Tuning
Sometimes, performance can be improved by tuning SQL parameters.
- Adjusting MySQL configuration: Parameters like
sort_buffer_size or tmp_table_size can be adjusted to better suit your query load.
7. Review and Continual Adjustment
Optimizing queries is not a one-time task. It's crucial to continually review the performance of your queries and adjust as needed, especially as the dataset grows and changes over time.
By implementing these techniques, you can significantly reduce the load time and improve the performance of your MySQL database. Remember, every database is unique, so it pays to tailor these strategies to your specific circumstances. Regularly monitoring and tweaking your queries ensures sustained database efficiency and speed.
Automating Slow Query Analysis
Consistent database performance is crucial for maintaining the reliability and speed of your web applications. Manually analyzing slow query logs can be time-consuming and may not adequately prevent performance bottlenecks as they develop. Automating the analysis of slow queries facilitates proactive database management, helping to ensure that your database remains efficient over time. In this section, we explore common methods and tools to automate the analysis of slow queries.
Using Event Schedulers
MySQL provides an inbuilt event scheduler that can be used to periodically check and analyze slow query logs. Setting up an event scheduler to automatically run analysis scripts can help identify slow queries at regular intervals. Here's an example of how you might set up such a scheduler:
DELIMITER //
CREATE EVENT analyze_slow_queries
ON SCHEDULE EVERY 1 HOUR
DO
BEGIN
CALL Analyze_and_Report_Slow_Queries();
END//
DELIMITER ;
This script would call the Analyze_and_Report_Slow_Queries stored procedure, which you would need to define according to your specific analysis criteria. This procedure might encapsulate logic for identifying queries that exceed a certain execution time and then logging these details into a performance analysis table or notifying your team via email or a web application.
Utilizing Monitoring Tools
Several specialized monitoring tools integrate features for automating the analysis of MySQL performance, including slow query logging. Tools such as Percona Monitoring and Management (PMM), SolarWinds Database Performance Analyzer, and Redgate SQL Monitor offer automated analysis features:
- Continuous Monitoring: These tools offer around-the-clock monitoring and will automatically flag slow-performing queries as they happen.
- Alerting Mechanisms: Set up alerts to be notified when certain thresholds are crossed, such as query response times, full table scans, or queries missing indexes.
- Dashboard Visualization: Most tools provide a comprehensive dashboard to visualize slow queries and their impact over time, allowing quick insights and actions.
Scripting Automation
For more customized solutions, scripting the download, parsing, and analysis of slow query logs can be achieved using a variety of scripting languages like Python, Bash, or Perl. An example Python script might look like:
import pymysql
import pandas as pd
db_connection = pymysql.connect(host='hostname', user='user', password='password', db='database')
query = "SELECT * FROM slow_log WHERE query_time > 1.0;"
df = pd.read_sql(query, con=db_connection)
print(df)
This script connects to the MySQL database, fetches queries taking more than a second from a slow_log table, and prints them out. These scripts can be scheduled to run via cron jobs or integrated into system workflows using CI/CD pipelines.
Implementing Continuous Integration (CI) Pipelines
Incorporate slow query log analysis into your CI/CD pipelines to ensure that new code deployments do not degrade database performance. Tools like Jenkins, GitHub Actions, or GitLab CI can be programmed to trigger specific database tests and alerts if slow queries are detected:
on: [push]
jobs:
check_db_performance:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Check for slow queries
run: python analyze_slow_queries.py
This CI/CD configuration triggers a Python script to analyze slow queries each time code is pushed to the repository, ensuring continual monitoring and immediate feedback.
Conclusion
Automating the analysis of slow query logs not only saves time but also significantly enhances the ability to maintain optimal database performance. By implementing one or more of the methods discussed, you can ensure that your database operations remain efficient and your applications perform at their best.
Case Studies
In this section, we explore real-world examples where the analysis of MySQL slow query logs has led to significant improvements in database performance across various applications. These case studies illustrate the practical benefits of monitoring and optimizing slow queries in live environments.
Case Study 1: E-Commerce Platform Optimization
Scenario: A large e-commerce website experienced slow page loads during peak sales events, which negatively affected customer satisfaction and sales conversion rates.
Challenge: The platform's database suffered from frequent slow queries, particularly during high-traffic periods, causing bottlenecks.
Solution: By enabling the MySQL slow query log, the team identified several slow-running queries on product pages and during checkout processes. The key parameters long_query_time was set to 2 seconds to capture any query running longer than this threshold.
Optimization: The analysis revealed:
- Multiple queries did not utilize indexes effectively.
- Some queries were repeatedly scanning large portions of the database.
By applying proper indexes and rewriting inefficient SQL queries, the team significantly reduced the execution time. For example, a critical query went from 3.5 seconds to under 200ms:
-- Before Optimization
SELECT * FROM products WHERE category_id = 123 ORDER BY price DESC;
-- After Adding Index
CREATE INDEX idx_category_id ON products(category_id);
-- Optimized Query
SELECT * FROM products USE INDEX (idx_category_id) WHERE category_id = 123 ORDER BY price DESC;
Result: Page load times improved by over 50%, enhancing user experience during critical sales periods and increasing sales conversion rates.
Case Study 2: Financial Services Reporting
Scenario: A finance company struggled with end-of-month reporting, which took significantly longer than expected, delaying insight delivery to decision-makers.
Challenge: The database executed complex queries aggregating large sets of transactional data, slowing down monthly report generation.
Solution: The slow query log was configured with a long_query_time of 5 seconds to identify problematic queries. The logs pinpointed several key queries without proper indexing and suboptimal joins.
Optimization: One major query involved aggregating transaction volumes across multiple accounts, which was optimized as follows:
-- Before Optimization
SELECT account_id, SUM(amount) as total FROM transactions GROUP BY account_id;
-- After Optimization
ALTER TABLE transactions ADD INDEX idx_account_id(account_id);
-- Optimized Query
SELECT account_id, SUM(amount) as total FROM transactions USE INDEX (idx_account_id) GROUP BY account_id;
Result: This optimization reduced the query time by approximately 65%, drastically cutting down the overall time required for monthly report generation.
Case Study 3: Health Care System Query Improvement
Scenario: A health care provider's database experienced sporadic slowdowns, impacting patient data retrieval speeds and operational efficiency.
Challenge: Slow queries impeded the performance of the system, particularly when accessing patient records and historical health data.
Solution: Implementation of slow query logging with a relatively low long_query_time helped in capturing a broad spectrum of inefficient queries.
Optimization: Analysis identified redundant data retrieval operations and opportunities for query refinement. Here’s an example of an optimized query:
-- Before Optimization
SELECT * FROM patient_records WHERE patient_id = 101 AND visit_date > '2022-01-01';
-- After Optimization
SELECT record_id, diagnosis, treatment FROM patient_records WHERE patient_id = 101 AND visit_date > '2022-01-01';
Result: The revised queries minimized the data load and reduced query execution times by up to 70%, significantly improving response times for clinical staff accessing critical patient information.
Conclusions
These case studies demonstrate that regular monitoring and analysis of slow query logs can uncover opportunities for significant performance improvements. Adjusting long_query_time, optimizing SQL command structures, and focusing on proper indexing are effective strategies as shown by these real-world applications. The right combination of tools and techniques can transform database management and operational efficiency.
Conclusions and Best Practices
As we have explored throughout this guide, MySQL Slow Query Logs serve as a pivotal tool in identifying and optimizing inefficient queries that impede database performance. By understanding and implementing the strategies discussed, organizations can substantially enhance the responsiveness and scalability of their database systems.
Key Insights Learned
-
Importance of Slow Query Logs: Slow query logs provide crucial insights into the performance of your SQL queries, highlighting those that exceed a predetermined execution time threshold.
-
Configuration and Customization: Properly configuring the slow query log, including setting parameters like long_query_time and log_queries_not_using_indexes, is vital to capture meaningful and actionable data.
-
Tools for Analysis: Utilizing tools such as mysqldumpslow or third-party software can simplify the process of analyzing slow query logs, giving clearer insights into performance bottlenecks.
-
Query Optimization: Regular analysis of slow query logs and subsequent optimization of queries can significantly reduce load times and improve overall database efficiency.
-
Automation: Automating the process of slow query analysis ensures continuous performance monitoring and improvements.
Best Practices for Ongoing Database Performance Management Using Slow Query Logs
-
Regular Monitoring: Implement a regular schedule for reviewing slow query logs. This proactive approach helps in catching and resolving performance issues before they escalate.
-
Set Appropriate Parameters: Adjust the long_query_time setting based on the typical performance expectations of your application. This value should be fine-tuned over time, as you gather more data about your application’s performance.
-
Indexing Strategies: Frequently evaluate and optimize your indexing strategies based on the queries logged as slow, particularly those not using indexes effectively.
-
Educate Developers: Ensure that all team members understand the importance of optimizing SQL queries. Hold regular training sessions on best practices in SQL development and performance optimization.
-
Leverage Automation Tools: Utilize scripts or tools to automate the parsing and analysis of slow logs. Automation can help in consistently applying performance tuning measures without manual intervention.
-
Performance Baselines: Establish performance baselines to better understand when a query is underperforming. This provides a metric for continuous improvement and helps validate the effectiveness of optimizations.
-
Iterative Improvement: Treat database performance management as an ongoing process. Continually refine queries, configurations, and indexing strategies to adapt to new requirements and usage patterns.
-
Cross-Departmental Collaboration: Encourage collaboration between developers, DBAs, and system administrators to ensure holistic performance tuning and management.
By diligently applying these insights and best practices, database administrators can leverage MySQL Slow Query Logs to enhance database operations effectively. The ultimate goal is to ensure that databases not only perform efficiently but also scale seamlessly as application demands grow.