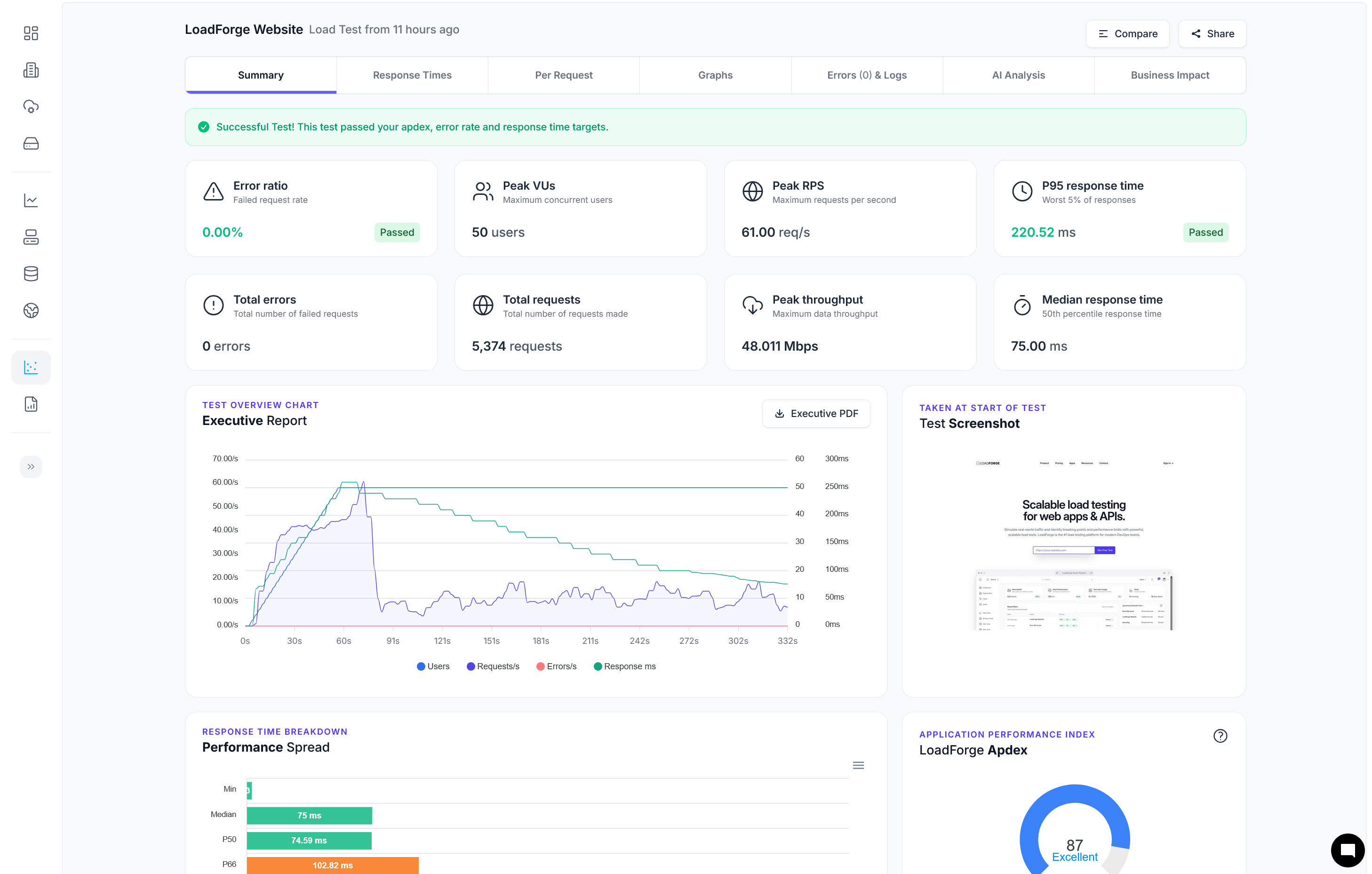
Introduction to Load Testing Nginx Servers
In an era where the efficiency of web servers can define the success of your online operations, ensuring that your Nginx server can withstand high traffic and deliver content reliably is paramount. Load testing emerges as a crucial endeavor to optimize performance and scalability of Nginx, one of the most popular web servers in the world today.
What is Nginx?
Nginx (pronounced as "Engine-X") is an open-source web server known for its high performance, stability, and low resource consumption. It surpasses many traditional servers in handling concurrent connections and its ability to serve static content quickly. However, its capabilities extend beyond merely serving web pages; Nginx functions as a reverse proxy, load balancer, and HTTP cache, which makes it particularly versatile in various deployment scenarios.
Common Use Cases
- Web Serving: Due to its asynchronous architecture, Nginx excels in delivering static content, making it a top choice for websites with high traffic volumes.
- Reverse Proxy Configurations: It efficiently manages the flow of network traffic between clients and other servers, enhancing security, and application performance.
- Load Balancing: Nginx distributes client requests or network load efficiently across multiple servers, ensuring the durability and scalability of applications.
Importance of Load Testing
Performance tuning of Nginx servers is not merely an optional supplement but a requisite for maintaining uptime and responsiveness under different load conditions. Here’s why load testing is irreplaceably vital:
- Scalability Analysis: Load testing helps in identifying the maximum operating capacity of your server, determining how your system performs when subjected to various stress levels before it is deployed.
- Bottleneck Identification: It can pinpoint where your configuration underperforms or lags, assisting in tweaking Nginx or the underlying hardware.
- Ensuring Reliability: By simulating different access patterns and traffic loads, load testing verifies if your server can handle high user demand without compromise.
By preparing your Nginx server to handle expected (and unexpected) internet traffic through rigorous load testing, you can ensure that your server maintains a smooth and effective response rate, avoiding potential downtimes and performance degradation that impact user experience and reliability. Next, let's delve into the crucial Nginx configurations that could impact your server's performance in our following section.
Understanding Your Nginx Configuration
Before initiating a load test on your Nginx server, it is essential to understand and optimize the key Nginx configurations that significantly impact your server's performance. Configuring Nginx correctly ensures that your web server handles requests efficiently, scales well under load, and provides a stable and fast experience for end-users. This section delves into several critical Nginx directives and parameters: worker_processes, worker_connections, keepalive_timeout, and the implementation of gzip compression.
worker_processes
This directive determines how many worker processes Nginx will create. Each worker process can handle thousands of network connections. The optimal number depends on the number of CPU cores available. For maximizing the use of hardware, it's generally recommended to set the worker_processes equal to the number of CPU cores.
worker_processes auto; # Adjusts to the number of available CPU cores
worker_connections
The worker_connections directive specifies the number of connections each worker process can handle simultaneously. This setting is crucial for determining the maximum load your server can handle at any given time.
events {
worker_connections 1024; # Each worker can handle 1024 connections
}
keepalive_timeout
The keepalive_timeout directive determines how long a connection to the client should be kept open without requests. This setting can affect the resource usage and responsiveness of your server. Proper tuning of this parameter can help improve connection times and reduce server load.
keepalive_timeout 75s; # Connections are kept open for 75 seconds
gzip Compression
Using gzip compression helps reduce the size of the data transmitted between your server and clients, which can significantly improve your website's load times and reduce bandwidth usage. Here is an example configuration to enable gzip compression:
gzip on;
gzip_types text/plain application/xml;
gzip_proxied any;
By understanding and optimizing these configurations, you prepare your Nginx server for more effective load testing. Each setting has a direct impact on how your server responds under various load conditions. Optimizing these parameters ensures that you achieve more realistic and reliable results from your tests, enabling informed decisions to enhance your server's performance further.
Preparing Your Test Environment
Before conducting a load test on your Nginx server, it is essential to set up a test environment that mirrors your production setup as closely as possible. This section will guide you through configuring your Nginx server for load testing and ensuring the test environment reflects real-world usage.
Step 1: Clone Your Production Environment
To achieve meaningful and accurate results, your testing environment needs to replicate the production environment in every significant aspect. Start with these steps:
- Hardware and Network Setup: Ensure the hardware specifications (CPU, RAM, Disk) and network configurations (bandwidth and latency) are similar to your production servers.
- Operating System and Dependencies: Install the same operating system and dependencies used in production to avoid discrepancies caused by different software environments.
Step 2: Configure Nginx Settings
Modify your Nginx configurations to reflect your production settings, paying special attention to parameters that directly affect performance. Here are some key directives to check:
-
worker_processes: This should be set to the number of processor cores available. For a load test, you may want to experiment with different values to simulate various levels of concurrency.
worker_processes auto;
-
worker_connections: Determines the maximum number of simultaneous connections that can be opened by a worker process. It is limited by the ulimit settings of the operating system.
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
-
keepalive_timeout: Adjusts the time a keep-alive connection stays open. Optimal settings can reduce the total number of connections during a load test.
keepalive_timeout 65;
-
gzip: Enabling gzip compression can significantly affect performance by reducing the amount of data transferred over the network.
gzip on;
gzip_types text/plain application/xml;
Step 3: Validate Configuration
Before running the load test, make sure that your Nginx configuration is optimized and free of errors:
nginx -t
This command checks for syntax errors and ensures that Nginx can run with the specified configuration files.
Step 4: Prepare Test Resources
-
Static and Dynamic Resources: Ensure all required resources such as HTML files, scripts, and databases are available and configured as they are in the production.
-
Security and Access Control: Align security settings, such as firewall rules and access controls, with production standards to avoid skewed test results due to blocked or failed requests.
Step 5: Isolate the Test Environment
To prevent the load test from affecting your actual production services, isolate the testing environment. This could be done through network segmentation or using a completely separate instance of your infrastructure that mimics production settings.
Step 6: Continuous Monitoring Setup
Set up monitoring tools to record the system's performance during the load test. Useful metrics include CPU usage, memory consumption, disk I/O, and network bandwidth. Tools like htop, iftop, or integrated solutions like Prometheus can be configured to provide insights into the system's behavior under load.
apt install htop iftop
Conclusion
Setting up a well-configured and realistic test environment is crucial for conducting effective load tests that provide actionable insights. Each step in this process from replicating your production environment to continuously monitoring your system under test, prepares you for a successful deployment of your load testing campaign using LoadForge.
Writing a Locustfile for Nginx
As we delve into the specifics of crafting a Locustfile for load testing Nginx servers, it's important to understand that the primary goal is to simulate real-world traffic under various conditions to gauge how well your server holds up. This part of the guide will walk you through creating a comprehensive Locustfile that encapsulates different types of web requests and load scenarios.
Understanding the Basics of a Locustfile
A Locustfile is essentially a Python script used by Locust to define user behavior and test scenarios. It is configured to spawn User classes that simulate how real users interact with your application.
Basic Structure of a Locustfile
A typical Locustfile includes:
- Import Statements: Necessary to access Locust's functions and classes.
- Task Set: Defines a collection of tasks (actions) each simulated user will perform.
- User Class: Represents a type of user and includes the tasks they perform.
- Execution Configuration: Determines how the load test is carried out (number of users, spawn rate, etc.).
Below is a simple example of a Locustfile structure:
from locust import HttpUser, task, between
class WebsiteUser(HttpUser):
wait_time = between(1, 5)
@task
def index_page(self):
self.client.get("/")
@task(3)
def heavy_load_page(self):
self.client.get("/heavy")
Tailoring Your Locustfile for Nginx
To customize this Locustfile for testing an Nginx server, consider the following additions:
- Diverse HTTP Requests: Include various HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT, DELETE to simulate different types of interactions.
- Static and Dynamic Content: Request static assets (CSS, images) and dynamic pages to see how Nginx handles different content types.
- Concurrent Users: Simulate multiple users accessing the same endpoint simultaneously.
- Error Handling: Incorporate tasks that purposely make bad requests to test how your server deals with potential errors.
Example of an Nginx-specific Locustfile
Here's an enhanced example demonstrating these concepts:
from locust import HttpUser, task, between
class NginxUser(HttpUser):
wait_time = between(1, 3)
@task(5)
def view_index(self):
self.client.get("/")
@task(3)
def view_blog(self):
self.client.get("/blog")
@task(1)
def post_comment(self):
self.client.post("/comment", {"text": "Great blog post!"})
@task
def static_content(self):
self.client.get("/static/image.png")
def on_start(self):
self.client.post("/login", {"username": "user", "password": "password"})
Testing Different Load Scenarios
To effectively test the resilience of your Nginx server, you should vary:
- User Load: Increase the number of simulated users gradually to see how Nginx scales.
- Request Types: Mix different types of requests within the same test to closely mimic varied traffic.
- Behavior Diversity: Introduce randomness in user behavior to simulate a more realistic usage pattern.
Integrating with LoadForge
Once your Locustfile is ready, you can easily upload it to LoadForge and configure the test parameters, such as the number of users, the duration of the test, and the geographic distribution of the load. This setup allows you to execute a distributed load test tailored specifically for your Nginx server.
By following these guidelines, you can prepare a robust Locustfile that challenges your Nginx setup and highlights potential bottlenecks and performance issues. This proactive approach ensures your server is optimized for handling real-world traffic and provides your users with a fast and reliable experience.
Executing the Load Test
Once you have crafted a tailored Locustfile to test your Nginx server, the next crucial step is to execute the load test using LoadForge. This step is vital in putting theory into practice and obtaining actionable insights on how your server performs under stress. Below are detailed instructions for deploying your Locustfile and executing a distributed load test against your Nginx server using LoadForge.
Step 1: Upload Your Locustfile to LoadForge
To begin, you need to upload your Locustfile to LoadForge. This file contains the specific scripts that simulate the web traffic and requests to your Nginx server:
- Log into your LoadForge account.
- Navigate to the Scripts section in the dashboard.
- Click on Create New Script.
- Name your test script and select Locust as the type.
- Copy and paste the contents of your Locustfile into the script text area provided by LoadForge.
- Save the script.
Step 2: Configure the Test Parameters
With your script uploaded, the next step involves setting up the parameters of your load test:
- Go to the Tests tab and click on Create Test.
- Select the script you uploaded in Step 1 from the dropdown menu.
- Set the duration of the test, usually in minutes or hours, depending on how long you want to stress test your Nginx server.
- Configure the number of users (simulated traffic) and the hatch rate (rate at which new users are spawned).
- Choose the location of the servers from where you want to launch the test, if LoadForge offers multiple locations. This helps in testing how your application handles traffic from different geographical locations.
Step 3: Launch the Test
Once your test is configured, launching it is straightforward:
- Review all the settings to make sure they align with your testing objectives.
- Click on the Start Test button to initiate the load test.
- LoadForge will distribute the workload across its cloud infrastructure based on your setup, executing the Locustfile against your Nginx server.
Step 4: Monitor the Test Progress
Monitoring the test in real-time is critical to understanding how your server is handling the load:
- LoadForge provides a real-time dashboard that displays vital metrics such as the number of users, requests per second, response times, and error rates.
- Keep an eye on the server's response time and error rates as they are crucial indicators of performance under load.
- Utilize the charts and graphs presented by LoadForge to visualize the load impact as the test progresses.
<pre><code>
# Example of an active monitoring dashboard snippet:
Requests: 450,000
Failures: 350
Median Response Time: 120ms
Average Response Time: 150ms
Min/Max Response Time: 100ms/300ms
</code></pre>
Step 5: Completing the Test
After the predetermined duration, LoadForge will automatically conclude the test:
- The service collects and compiles the results.
- A final report will be generated, showcasing comprehensive data on how your Nginx server coped with the simulated load.
Next Steps
Upon completing the load test, your next course of action involves analyzing the detailed report generated by LoadForge (this is covered in the next section, "Analyzing Test Results"). This analysis is crucial in identifying potential bottlenecks and making informed decisions to optimize server performance.
By following these steps, you can successfully execute a distributed load test against your Nginx server, gaining invaluable insights into its performance and scalability under various stress conditions. Remember, frequent load testing is essential in ensuring your infrastructure remains robust and responsive as user demand and data traffic fluctuate.
Analyzing Test Results
Understanding the results of your load test is a pivotal step in load testing your Nginx server. The data gathered during a load test can provide insights into how your server configuration stands up to stress and what changes might be necessary to enhance performance. This section will guide you through interpreting the data provided by LoadForge, focusing on key metrics such as response time, throughput, error rates, and server resource utilization.
Key Metrics to Analyze
-
Response Time
- Definition: The time it takes for the server to respond to a request.
- Importance: Indicates the efficiency of request handling under load. Shorter response times are generally better, suggesting that the server can handle requests quickly even under stress.
-
Throughput
- Definition: The number of requests that the server can handle per unit of time.
- Importance: A higher throughput indicates that the server can handle a larger number of requests, which is crucial for high-traffic environments.
-
Error Rates
- Definition: The percentage of requests that result in errors.
- Importance: A high error rate could indicate problems in the server setup or an inability of the server to handle concurrent requests efficiently.
-
Server Resource Utilization
- Definition: Metrics like CPU usage, memory usage, disk I/O, and network I/O.
- Importance: Helps identify bottlenecks in server resources that could be causing slowdowns or failures under load.
Interpreting the Results
Visualizing Data
LoadForge provides graphs and charts that make it easier to visualize the response times, throughput, and error rates over the duration of the test. For example:
- A response time graph might show response times increasing as the load increases, indicating potential performance bottlenecks.
- A throughput graph might plateau or drop at a certain point, showing the maximum handling capacity of the server before performance degrades.
- Error rate charts can help pinpoint the exact load level at which the server starts to return errors significantly.
Sample Data Insights
Response Time: Average response time increased from 100ms at 100 users to 300ms at 500 users.
Throughput: Requests per second increased up to 300 users, then stabilized, indicating a limit in capacity.
Error Rates: Began to increase significantly when exceeding 400 users, suggesting server strain.
Resource Utilization: CPU usage reached 90% at 400 users, while memory remained under 70% usage.
Diagnosing Common Issues
- High Response Times at low concurrency might suggest inefficient application logic or misconfigured server settings.
- Throughput Plateaus could indicate network bandwidth limits or a reached limit of the server's processing capacity.
- Increasing Error Rates as the load increases might indicate software or hardware failures under stress, such as database locks or exhausted server resources.
Actionable Steps
Upon identifying issues:
- Adjust Nginx Settings: Tweak
worker_processes, worker_connections, or other relevant settings based on observed bottlenecks.
- Optimize Application Code: If response times increase unusually, review application code for potential optimizations.
- Upgrade Server Resources: If server resource utilization is consistently high, consider upgrading hardware capabilities or scaling out.
Summary
By thoroughly analyzing the test results provided by LoadForge, you can gain valuable insights into the scalability and robustness of your Nginx server. This analysis not only helps in pinpointing existing issues but also in proactively making adjustments to handle future demands effectively. Remember, each metric provides a piece of the overall performance puzzle, helping guide your optimization efforts for enhanced server performance and reliability.
Optimizing Based on Findings
After conducting a thorough load test on your Nginx server using LoadForge, you will have gathered a significant amount of data to analyze. This section will guide you through the process of interpreting this data and making informed decisions to optimize your Nginx configuration. By tweaking your settings based on real-time feedback from load testing, you can ensure that your server remains robust and highly available under various load conditions.
Step 1: Identifying Bottlenecks
Start by identifying the performance bottlenecks in your system. Key metrics to consider include:
- Response Time: Long response times might indicate a need for better load balancing or hardware upgrades.
- Throughput: Low throughput can be a signal of network bandwidth issues or inefficient Nginx configurations.
- Error Rates: High error rates could be the result of server overload, requiring attention to load distribution and fault tolerance configurations.
Step 2: Adjusting Nginx Configurations
Analyzing the test results can often lead to straightforward adjustments in your Nginx configuration. Below are some common optimizational tweaks:
Increase worker_processes
This directive should generally be set to the number of CPU cores on your server.
worker_processes auto; # enables Nginx to detect the number of CPU cores
Optimize worker_connections
The number of connections each worker process can handle can be configured with the worker_connections directive. The ideal number often depends on the nature of your applications and the expected load.
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
Enable gzip Compression
Enabling gzip compression reduces the size of the payloads transmitted from your server, improving the load times and bandwidth usage:
gzip on;
gzip_types text/plain application/xml text/css application/javascript;
gzip_proxied any;
Tuning keepalive_timeout
Adjust the keepalive timeout to balance server performance and resource utilization. Lower timeouts can free up connections faster, but might increase the load due to more frequent TCP connections set up and tear down.
keepalive_timeout 15;
Step 3: Load Scenario Adjustments
Based on the various load scenarios you've tested, consider implementing dynamic configurations that adapt to the load:
-
Rate Limiting: During spikes in traffic, implementing rate limiting can protect your server from being overwhelmed:
limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=one:10m rate=5r/s;
-
Caching: Implement caching strategies for static assets to reduce the load on your servers during peak times.
location /static/ {
expires 30d;
}
Step 4: Implementing Changes and Retesting
Once you've made your adjustments, it's crucial to retest using the same scenarios to quantify the improvements. Try to iteratively make changes and monitor how each change impacts the performance metrics.
Step 5: Continuous Optimization
Regularly update your load tests to reflect new usage patterns and code changes. Continuous performance testing should be a part of your deployment process to ensure that your Nginx configurations are always tailored to the current demands.
By following these guidelines and making well-informed adjustments based on empirical data from your load tests, you can significantly enhance both the efficiency and resilience of your Nginx servers.
Best Practices for Continuous Testing
Incorporating continuous testing into your development cycle is not just beneficial; it's essential for maintaining and improving the performance and reliability of your Nginx servers. By consistently applying load testing, you ensure that your web server configurations are optimized and that your infrastructure can handle peak loads smoothly. Here are some best practices to integrate continuous load testing into your workflow:
Automate Load Testing
Automation is key to integrating load testing into your CI/CD pipeline efficiently. Use automation tools to trigger load tests after every significant change in your application or infrastructure:
-
Integration with CI Tools: Use popular CI/CD platforms like Jenkins, GitLab CI, or CircleCI to automate the execution of load tests. You can set up jobs that automatically initiate a load test using LoadForge whenever new code is committed to your repository.
Example automation script in Jenkins:
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage ('Load Test') {
steps {
sh 'curl -X POST https://api.loadforge.com/new/test -H "Authorization: Bearer your_api_key"'
}
}
}
}
-
Scheduled Testing: Apart from triggering tests via CI pipelines, consider scheduling regular load tests (e.g., nightly or weekly) to continuously monitor the performance impacts of cumulative changes.
Monitor and Alert
Effective monitoring and setting up alerts for performance metrics are crucial to promptly addressing issues that load tests reveal:
- Monitor Test Results: Utilize LoadForge’s dashboards to monitor ongoing and completed tests. Keep an eye on key metrics like response times, throughput, and error rates.
- Set Alerts: Configure alerting mechanisms to notify your team when performance metrics deviate from expected thresholds. This ensures that potential issues can be addressed before they impact end-users.
Test in Realistic Environments
Ensure that the test environment closely replicates the production environment:
- Match Configuration: Keep the test environment’s Nginx configuration as close to production as possible.
- Simulate Real User Behaviour: Use Locust to mimic real user interactions with your application to get accurate insights on how changes affect user experience.
Review and Analyze Regularly
Regular reviews of test results and performance trends are indispensable:
- Analyze Trends: Look for trends in the test data over time to identify performance degradation or improvements.
- Conduct Retrospectives: After significant load tests, hold retrospectives with your team to discuss what the results indicate about your system’s capacity and resilience, and what actions are necessary.
Documentation and Knowledge Sharing
Document every test configuration, change, and outcome. Maintain a repository of test scenarios and their impacts that your team can refer to, which helps in understanding the effect of various configurations and code changes:
- Maintain Test Logs: Keep detailed records of test parameters, configurations, and results.
- Share Learnings: Regularly share findings and updates with your team to ensure everyone is informed about performance benchmarks and infrastructure capabilities.
By following these best practices, you can create a robust framework for continuous load testing, ensuring your Nginx servers are always tuned for optimal performance and ready to handle real-world demands. This proactive approach not only prevents disruptions but also fosters a culture of performance-aware development.