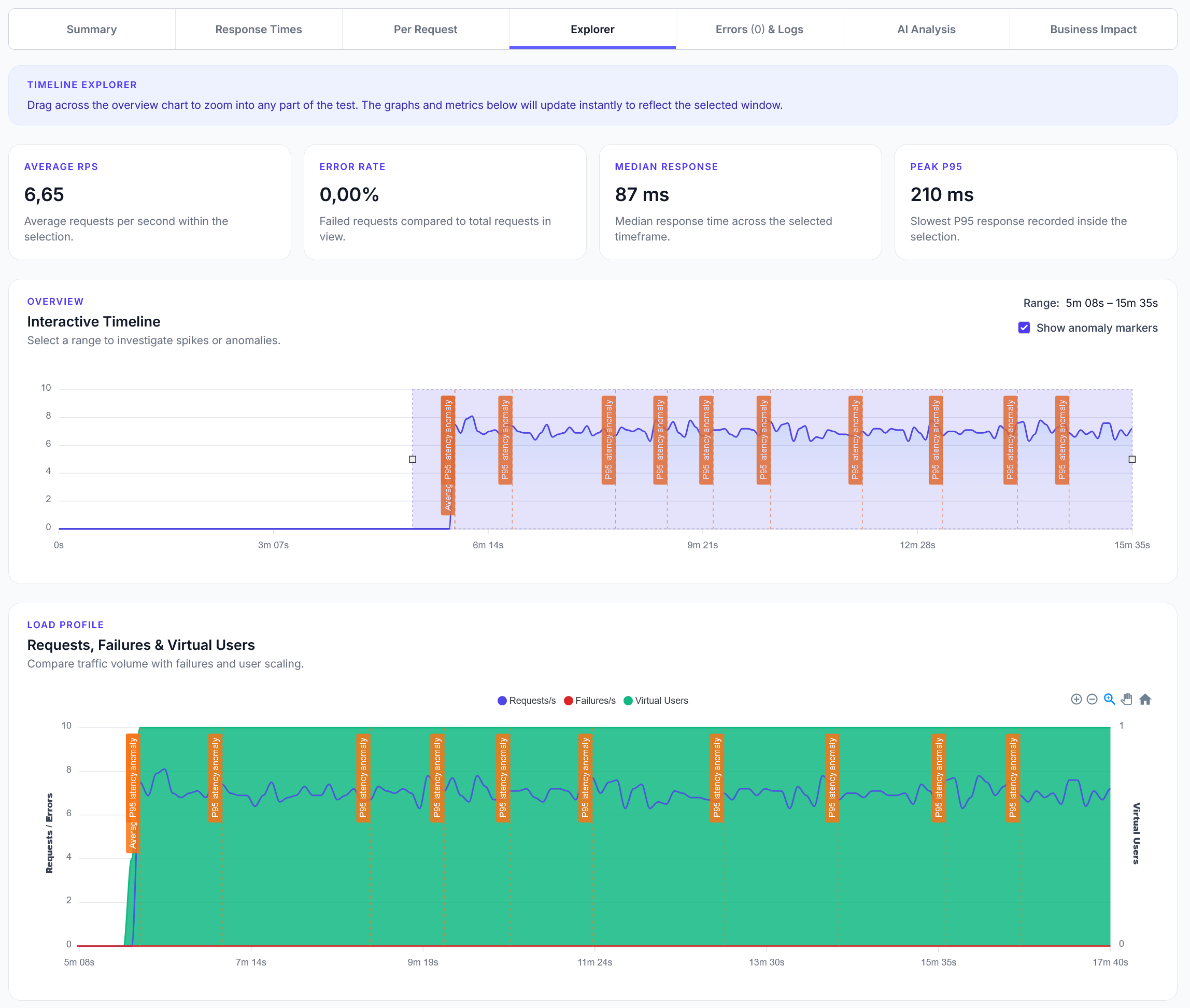
Explorer reports addition
We have added a new Explorer feature to reports, with a timeline scrubber and easy anomaly detection.
Basic serverless function testing for AWS Lambda, Vercel Functions, and Netlify Functions
LoadForge can record your browser, graphically build tests, scan your site with a wizard and more. Sign up now to run your first test.
This guide shows how to test serverless functions and measure cold start performance. Perfect for testing serverless APIs and function-based architectures.
from locust import task, HttpUser
import time
import random
class ServerlessTestUser(HttpUser):
def on_start(self):
# Serverless function endpoints to test
self.functions = {
"aws_lambda": {
"url": "https://your-api-id.execute-api.region.amazonaws.com/prod/function",
"name": "AWS Lambda"
},
"vercel": {
"url": "https://your-app.vercel.app/api/function",
"name": "Vercel Function"
},
"netlify": {
"url": "https://your-app.netlify.app/.netlify/functions/function",
"name": "Netlify Function"
}
}
# Test payloads
self.test_payloads = [
{"message": "Hello World"},
{"data": {"user_id": 123, "action": "test"}},
{"query": "simple test query"},
{} # Empty payload
]
@task(3)
def test_aws_lambda(self):
"""Test AWS Lambda function"""
if "aws_lambda" in self.functions:
function = self.functions["aws_lambda"]
payload = random.choice(self.test_payloads)
start_time = time.time()
with self.client.post(
function["url"],
json=payload,
name="AWS Lambda"
) as response:
response_time = (time.time() - start_time) * 1000
if response.status_code == 200:
print(f"AWS Lambda: {response_time:.0f}ms")
# Check for cold start indicators
if response_time > 1000: # > 1 second might be cold start
print(f"AWS Lambda: Possible cold start ({response_time:.0f}ms)")
else:
response.failure(f"AWS Lambda error: {response.status_code}")
@task(3)
def test_vercel_function(self):
"""Test Vercel Function"""
if "vercel" in self.functions:
function = self.functions["vercel"]
payload = random.choice(self.test_payloads)
start_time = time.time()
with self.client.post(
function["url"],
json=payload,
name="Vercel Function"
) as response:
response_time = (time.time() - start_time) * 1000
if response.status_code == 200:
print(f"Vercel Function: {response_time:.0f}ms")
# Vercel functions typically have faster cold starts
if response_time > 500:
print(f"Vercel Function: Possible cold start ({response_time:.0f}ms)")
else:
response.failure(f"Vercel Function error: {response.status_code}")
@task(2)
def test_netlify_function(self):
"""Test Netlify Function"""
if "netlify" in self.functions:
function = self.functions["netlify"]
payload = random.choice(self.test_payloads)
start_time = time.time()
with self.client.post(
function["url"],
json=payload,
name="Netlify Function"
) as response:
response_time = (time.time() - start_time) * 1000
if response.status_code == 200:
print(f"Netlify Function: {response_time:.0f}ms")
if response_time > 800:
print(f"Netlify Function: Possible cold start ({response_time:.0f}ms)")
else:
response.failure(f"Netlify Function error: {response.status_code}")
@task(2)
def test_cold_start_behavior(self):
"""Test cold start behavior by waiting between requests"""
function_key = random.choice(list(self.functions.keys()))
function = self.functions[function_key]
# Wait to increase chance of cold start
wait_time = random.uniform(30, 120) # 30-120 seconds
print(f"Waiting {wait_time:.0f}s to test cold start for {function['name']}")
time.sleep(wait_time)
start_time = time.time()
with self.client.get(
function["url"],
name=f"Cold Start - {function['name']}"
) as response:
response_time = (time.time() - start_time) * 1000
if response.status_code == 200:
print(f"Cold start test {function['name']}: {response_time:.0f}ms")
# Analyze cold start performance
if response_time > 2000:
print(f"Cold start {function['name']}: SLOW ({response_time:.0f}ms)")
elif response_time > 1000:
print(f"Cold start {function['name']}: MODERATE ({response_time:.0f}ms)")
else:
print(f"Cold start {function['name']}: FAST ({response_time:.0f}ms)")
@task(1)
def test_function_scaling(self):
"""Test how functions handle concurrent requests"""
function_key = random.choice(list(self.functions.keys()))
function = self.functions[function_key]
# Make multiple rapid requests to test scaling
concurrent_requests = 3
results = []
for i in range(concurrent_requests):
start_time = time.time()
with self.client.get(
function["url"],
name=f"Scaling Test - {function['name']}"
) as response:
response_time = (time.time() - start_time) * 1000
results.append(response_time)
if response.status_code != 200:
response.failure(f"Scaling test failed: {response.status_code}")
if results:
avg_time = sum(results) / len(results)
max_time = max(results)
print(f"Scaling test {function['name']}: avg {avg_time:.0f}ms, max {max_time:.0f}ms")
@task(1)
def test_function_with_different_payloads(self):
"""Test functions with different payload sizes"""
function_key = random.choice(list(self.functions.keys()))
function = self.functions[function_key]
# Test with different payload sizes
payloads = [
{"size": "small", "data": "x" * 100},
{"size": "medium", "data": "x" * 1000},
{"size": "large", "data": "x" * 10000}
]
for payload in payloads:
start_time = time.time()
with self.client.post(
function["url"],
json=payload,
name=f"Payload Test - {function['name']}"
) as response:
response_time = (time.time() - start_time) * 1000
if response.status_code == 200:
print(f"Payload test {function['name']} ({payload['size']}): {response_time:.0f}ms")
else:
print(f"Payload test {function['name']} ({payload['size']}): ERROR {response.status_code}")
@task(1)
def test_function_error_handling(self):
"""Test how functions handle errors"""
function_key = random.choice(list(self.functions.keys()))
function = self.functions[function_key]
# Test with invalid data to trigger errors
error_payloads = [
{"invalid": "data", "trigger_error": True},
{"malformed": "json"},
None # No payload
]
error_payload = random.choice(error_payloads)
with self.client.post(
function["url"],
json=error_payload,
name=f"Error Test - {function['name']}"
) as response:
if response.status_code >= 400:
print(f"Error test {function['name']}: Properly returned {response.status_code}")
elif response.status_code == 200:
print(f"Error test {function['name']}: Handled error gracefully")
else:
print(f"Error test {function['name']}: Unexpected response {response.status_code}")
Typical cold start times: