Introduction to Load Testing PHP Websites
Load testing is an essential process for preparing any website for the rigors of high traffic, particularly for those built with PHP, a popular server-side scripting language. As PHP powers a significant portion of the web, including dynamic content-heavy sites and applications like WordPress and Facebook, ensuring these sites perform under pressure is crucial.
Why Load Testing Matters for PHP Sites
When a PHP website goes live, it's expected to handle requests efficiently, maintaining performance despite the number of users scaling up. Without proper preparation, high traffic can lead to slow page load times, decreased user satisfaction, and ultimately, loss of revenue and reputational damage. The objective of load testing is to preemptively discover and mitigate these issues by simulating user behavior at varying levels of traffic and interaction.
Common Challenges Faced by PHP Applications Under Load:
PHP applications, particularly those with complex databases and multiple integrations, face several challenges under heavy load:
- Resource Utilization: PHP can be resource-intensive, especially with inadequate optimization. Under load, systems might experience high CPU usage and memory overflow issues.
- Database Bottlenecks: Many PHP applications rely heavily on database interactions. Load can exacerbate inefficiencies in database queries, leading to slow response times and timeouts.
- Concurrency Issues: PHP applications may struggle with handling multiple simultaneous user requests, leading to session management problems and data inconsistency.
- Scalability: PHP applications might not scale efficiently horizontally or vertically without specific architectural considerations and appropriate configuration adjustments.
Importance of Proactive Testing
Proactive load testing allows developers and QA teams to identify and address these issues before they impact users. It's not just about ensuring the application can handle the expected number of users but also about understanding how the application behaves under stress, which components fail first, and what kind of failures they might provoke.
Load testing a PHP application typically involves:
- Simulating Realistic User Interactions: Crafting tests that accurately represent how end-users interact with the application, from simple page requests to complex transactions.
- Analyzing Performance at Various Load Levels: Gradually increasing the load to understand how performance changes in response, which helps in identifying non-linear behaviors and thresholds.
- Tuning and Optimization Based on Results: Using data from load tests to optimize everything from code and query performance to infrastructure and resource allocation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, load testing is not just a checkbox in the deployment checklist. It is a critical, ongoing practice that can significantly determine the success of a PHP website in live environments. By understanding and implementing structured load testing, developers can assure not only the performance but also the reliability and scalability of the application under real-world conditions. The next sections will delve deeper into setting up such testing environments specifically using LoadForge, crafting effective locustfiles, and optimizing your PHP application based on insightful data derived from load tests.
Setting Up Your Testing Environment
Properly setting up your testing environment is crucial for accurate and effective load testing of PHP websites. This section guides you through configuring a LoadForge test, including selecting the appropriate test parameters and preparing your environment to utilize a Locustfile designed for PHP applications.
Selecting the Right Test Parameters
Selecting test parameters is about defining the scope and scale of your test, which impacts how representative and effective the results will be. For PHP websites, you should consider:
- User Load: Decide how many virtual users (clients) will simulate traffic to your application. It's important to test different loads, from average daily users to peak traffic scenarios.
- Test Duration: Determine how long each test will run. Sustained tests help identify issues that may develop over time, such as memory leaks.
- Request Rate: Decide the rate at which users will make requests. This can vary based on user behavior patterns typical to PHP applications.
- Geographical Distribution: If your audience is global, testing from multiple locations can provide insights into how geographical distribution affects performance.
Setting Up Your Testing Environment
To ensure your LoadForge test runs smoothly, setup your testing environment with these steps:
- Ensure Server Accessibility: Verify that your PHP application's server is accessible from the internet to allow LoadForge to interact with it.
- Resource Monitoring: Setup monitoring on your server to observe resource usage (CPU, memory, disk, network). This helps in correlating performance impacts observed during testing.
- Backup Your Data: Always ensure that your testing environment is either a cloned production environment or has a reliable backup. Load testing can stress your system and potentially lead to data loss.
Configuring LoadForge to Use Your Locustfile
A locustfile defines the behavior of your simulated users during the test. It is vital that this script accurately reflects the user interaction patterns with your PHP application. Here is how you can configure your LoadForge setup to use your specifically tailored locustfile:
-
Prepare Your Locustfile: Write a script that simulates typical user behaviors on your PHP site, such as loading web pages, logging in, sending forms, etc. Below is a simple example of a locustfile that tests a PHP website:
from locust import HttpUser, task, between
class WebsiteUser(HttpUser):
wait_time = between(1, 5) # Simulate real user wait time between actions
@task
def load_homepage(self):
self.client.get("/")
@task(3) # Higher weight means this task runs more frequently
def view_products(self):
self.client.get("/products")
@task
def post_form(self):
self.client.post("/submit-form", {"name": "John Doe", "age": 30})
-
Upload to LoadForge: Login to your LoadForge account and upload your locustfile script.
-
Test Configuration: Use the LoadForge interface to input your test parameters (number of users, duration, etc.) and point the test to your PHP website's URL.
-
Save and Ready: After configuration, save your settings. Your environment is now set to execute a load test.
By following these steps, you will have a well-configured testing environment that is primed to accurately assess the performance of your PHP application under various load conditions. Next, we will proceed to execute the load test and monitor how the application performs.
Writing Your Locustfile
In this critical section, we'll dive into the specifics of writing a locustfile tailored for PHP websites. A well-crafted locustfile is essential for simulating real-world user behavior and ensuring your PHP application can handle the anticipated load. We'll focus on key user interactions such as browsing pages, submitting forms, and making AJAX calls.
Understanding the Basics of a Locustfile
A locustfile is a Python script that defines the behavior of simulated users in your load test. Each "user" is represented by a class that inherits from HttpUser, and within this class, tasks are defined to represent user actions. Below is a general structure of a locustfile:
from locust import HttpUser, task, between
class WebsiteUser(HttpUser):
wait_time = between(1, 5) # Simulate realistic think time between requests.
@task
def load_main_page(self):
self.client.get("/")
@task(3) # Higher weight, more frequent execution
def browse_products(self):
self.client.get("/products")
@task(2)
def post_form(self):
self.client.post("/submit", {"name": "testuser", "email": "test@example.com"})
Tailoring Locustfile for PHP Websites
When designing a locustfile for PHP websites, it’s important to mimic the interactions an average user would perform on your site. Here’s how you can structure tasks to simulate different types of requests:
1. Browsing Pages
Most websites will involve some level of page browsing. Simulating this involves making GET requests to different URLs on your PHP website.
@task
def view_blog(self):
self.client.get("/blog")
self.client.get("/blog/post1")
2. Submitting Forms
If your website includes forms (e.g., contact forms, login pages), you can simulate form submissions using POST requests:
@task
def submit_contact_form(self):
self.client.post("/contact", {
"name": "John Doe",
"email": "john.doe@example.com",
"message": "Hello, your service is awesome!"
})
3. Executing AJAX Calls
AJAX is heavily used in modern PHP applications for asynchronous operations. You can simulate these by sending requests to endpoints typically triggered via JavaScript:
@task
def load_ajax_content(self):
headers = {'X-Requested-With': 'XMLHttpRequest'}
self.client.get("/ajax/endpoint", headers=headers)
Tips for Effective Locustfiles
- Use Task Weights: By assigning different weights to your tasks, you can ensure that more critical paths (e.g., checking out a cart) are tested more frequently than others.
- Parameterize Input Data: To avoid issues like cached responses and unrealistic testing scenarios, use parameterized inputs for forms and URLs.
- Include Static and Dynamic Requests: Ensure your tests include static content (e.g., CSS, JavaScript) and dynamic content requests to get a realistic measure of your application's performance.
Conclusion
This locustfile provides a robust framework for simulating user behavior on a PHP-driven website. By customizing this base example to more closely reflect your specific application's functionality and user interaction patterns, you can conduct thorough load tests that help optimize your PHP site's performance under various load conditions. Armed with this tool, you can significantly enhance your site's reliability and user experience in high-traffic scenarios.
Executing the Load Test
Executing a load test effectively is crucial for diagnosing and enhancing the performance of your PHP website. LoadForge simplifies this process by providing an intuitive platform for running your tests. This section will guide you through launching the test, monitoring performance in real-time, and interpreting the initial results to measure impact on your PHP application.
Launching the Test
Before launching, ensure your LoadForge test is properly set up with the locustfile tailored for your PHP application. Follow these steps:
- Login to LoadForge: Navigate to the LoadForge dashboard.
- Select Your Test: Choose the test you have previously configured or create a new one if necessary.
- Review the Configurations: Double-check your test settings including test duration, number of users, and user spawn rate.
- Deploy the Test:
- Click on the Start Test button.
- Confirm your specifications and begin the test.
A typical command to launch a test from LoadForge might look like this:
loadforge --users 1000 --spawn-rate 10 --host https://your-php-application.com my_locustfile.py
Monitoring Real-Time Performance Metrics
As soon as you launch the test, LoadForge provides a real-time analytics dashboard where you can monitor key performance metrics. Pay attention to the following metrics:
- User Load: The number of virtual users interacting with your site.
- Response Times: Average, median, and max response times which highlight the speed of your site under pressure.
- Error Rates: Track failed requests and errors to identify critical issues during the test.
- Throughput: Measure the number of requests per second to gauge the capacity of your web servers.
Here's an example snapshot of what monitoring might look like:
----------------------------------------
| Users | Response Time | Throughput |
|--------------------------------------|
| 1000 | 115 ms | 300 rps |
| 2000 | 130 ms | 290 rps |
| 3000 | 150 ms | 270 rps |
----------------------------------------
Interpreting the Initial Results
After the completion of your load test, it's essential to understand the data collected and interpret them to gauge the performance of your PHP application. Key considerations include:
- Response Times: Did they significantly increase under higher loads? An upward trend might suggest bottlenecks.
- Error Rates: High error rates could indicate insufficient server resources or software bugs.
- Resource Usage: High CPU or memory usage can be a sign of inefficient code or inadequate hardware.
These metrics collectively provide a snapshot of your PHP website's resilience and areas that need attention. Consider this initial interpretation as a baseline for fine-tuning and further detailed analysis in subsequent iterations.
By following these detailed steps and analyzing your test outcomes, you can effectively execute a load test on your PHP website using LoadForge, ensuring your application can withstand real-world conditions and high traffic scenarios.
Analyzing Test Results
After successfully executing a load test on a PHP website using LoadForge, it's imperative to meticulously analyze the results to ensure the application's readiness for high traffic conditions. This section outlines the key steps and strategies for dissecting the data obtained during testing, pinpointing performance bottlenecks, and understanding specific metrics that are crucial for optimizing PHP applications.
Step 1: Accessing the Test Results
The first step is to retrieve the comprehensive test reports generated by LoadForge. These reports are available through the LoadForge dashboard and provide a wealth of information including request success rates, response times, and system utilization metrics.
Viewing Test Summaries
LoadForge presents a summary of the test that includes:
- Total Requests Made: Number of total requests sent during the test.
- Request Success Rate: Percentage of requests that were successfully handled by your server.
- Average Response Time: Average time taken to respond to requests during the test.
- Peak Response Time: Maximum response time recorded.
Step 2: Identifying Bottlenecks
Identifying bottlenecks is crucial in pinpointing areas that significantly impact the performance of your PHP application under load. Two main areas often serve as bottlenecks:
- Server Resources: Memory, CPU usage, and disk I/O can be critical bottlenecks. Analyze the server utilization metrics from LoadForge reports to spot any resource over-utilizations.
- Database Performance: Slow queries or high database load can cripple your application. If your locustfile includes database interactions, review the times and logs related to these actions.
Step 3: Analyzing Response Times and Failures
Response times and failure rates can reveal insights into the stability and efficiency of your PHP applications.
Detailed Review of Response Times
Analyze the response time distribution to understand how your application performs under different loads:
Response Time (ms) | Number of Requests
-------------------|-------------------
0-200 | 15000
201-400 | 3000
401-600 | 500
601+ | 100
Investigating Failures
Examine request failures to understand under what conditions your application fails:
- Error Rates: High error rates could indicate issues like server misconfigurations, exhausted resources, or unhandled exceptions in your code.
- Specific Errors: Review the logs for specific error messages or status codes that indicate particular problems.
Step 4: Performance Metrics Specific to PHP
PHP applications might exhibit some unique behavior under load due to their configuration and architecture:
- Session Handling: Analyze how session handling affects performance, especially under concurrent access conditions.
- Opcode Caching: Ensure that opcode caching mechanisms like OPcache are properly utilized and configured.
- Garbage Collection Metrics: Check how PHP's garbage collection is performing under load. A poorly performing garbage collection can lead to memory issues.
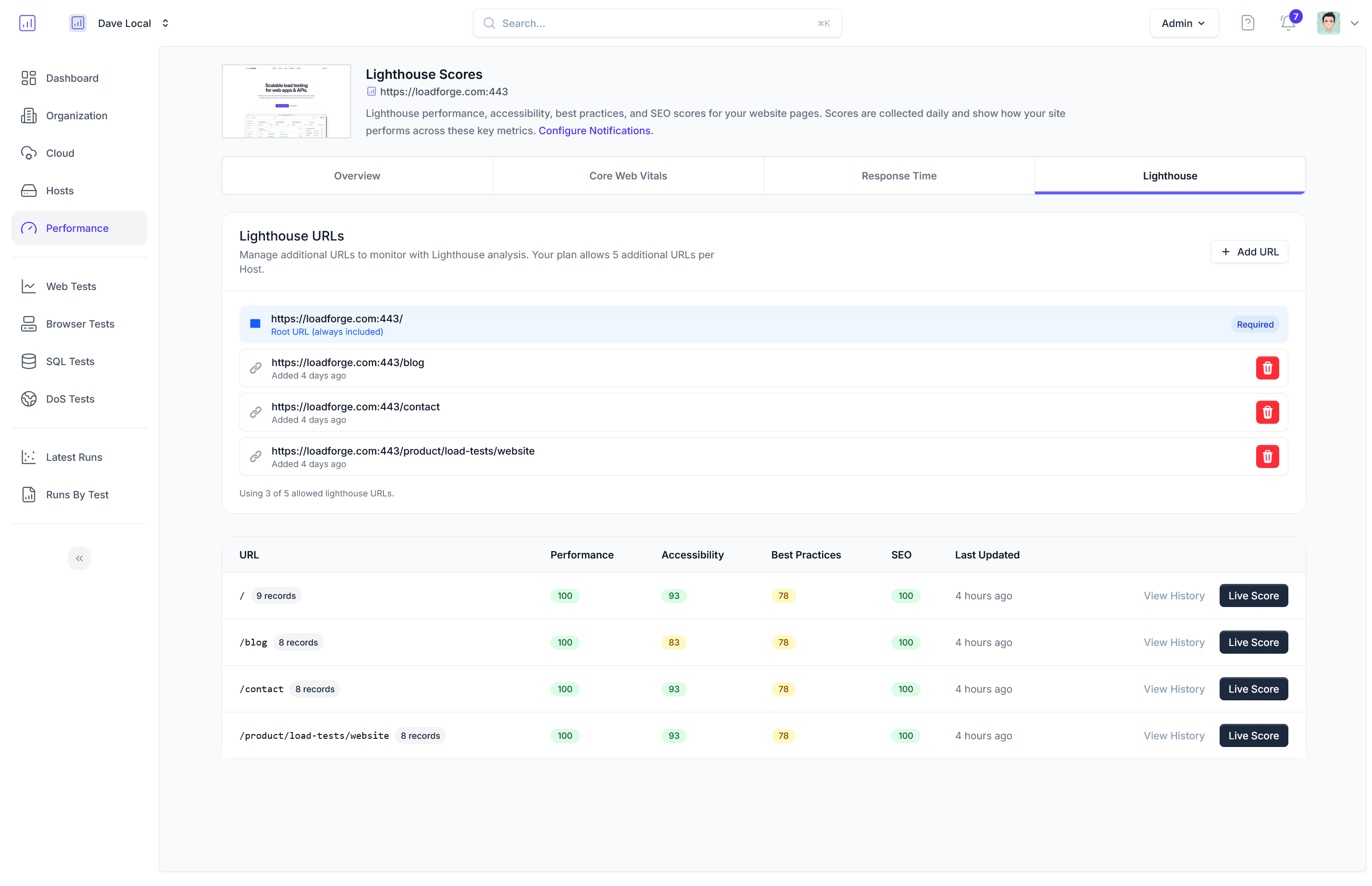
Step 5: Visualizing the Data
Using LoadForge’s graphical interfaces, visualize the data for better insights. Line graphs for response times, bar graphs for server load, and pie charts for request distribution are useful for presenting data comprehensively.
Conclusion
Thorough analysis of load test results is critical to tuning and optimizing PHP websites for high performance. By understanding these metrics, identifying bottlenecks, and investigating errors, you can implement effective optimizations to ensure your PHP application is robust and scalable enough to handle anticipated traffic volumes. Regular analysis and tuning guided by empirical data from tools like LoadForge will help maintain optimal performance as your application grows and evolves.
Optimizing PHP Performance
Upon completing the load test and analyzing the results, identifying performance bottlenecks is critical for enhancing the PHP application's ability to handle heavy traffic efficiently. Based on the insights gained from the testing phase, let's explore various optimization techniques specifically targeted towards improving PHP websites.
Caching Techniques
1. Opcode Caching:
PHP scripts are interpreted, which can be a slow process as each script needs to be compiled every time it is executed. Opcode caching reduces this overhead by storing precompiled script bytecode in memory, allowing the server to execute code faster.
-
Recommended Tool: Use OPcache, which is included by default from PHP 5.5 onwards. Ensure it is enabled in your php.ini file:
[opcache]
opcache.enable=1
opcache.memory_consumption=128
opcache.interned_strings_buffer=8
opcache.max_accelerated_files=4000
2. Data Caching:
Storing results of database queries, API calls, or heavy computational results can significantly reduce load times by avoiding repeated processing and database load.
-
Recommended Tools: Consider implementing caching with Redis or Memcached. Here’s an example using Redis:
$redis = new Redis();
$redis->connect('localhost', 6379);
$cacheKey = 'user_profile_' . $userId;
$userData = $redis->get($cacheKey);
if (!$userData) {
$userData = getUserDataFromDatabase($userId); // assume this function fetches data from DB
$redis->setex($cacheKey, 3600, serialize($userData)); // cache for 1 hour
} else {
$userData = unserialize($userData);
}
// Use $userData
Database Optimization
1. Indexing:
Proper indexing can reduce the data scan and speed up the retrieval process, thereby minimizing the response time especially when the load is high.
2. Query Optimization:
Ensure that queries are efficient and use minimal resources by checking the query execution plan and optimizing them.
Code Improvements
-
Refactor Loops and Conditions: Analyze the loops and conditional statements to check for unnecessary repetitions and redundant conditions.
-
Utilize Composer Autoload:
Make sure to implement Composer’s Classmap or PSR-4 autoloading. This avoids including or requiring files unnecessarily, helping to reduce the disk I/O.
Utilizing Load Balancers
Deploying a load balancer can distribute incoming network traffic across multiple servers, thus keeping any single server from getting overwhelmed. This is critical in managing traffic spikes and improving redundancy.
Resource Scaling
Based on the test results, consider horizontal scaling (adding more servers) or vertical scaling (upgrading existing servers with more resources) to meet the demand.
As observed, each optimization step relies on specific insights gained from load testing. By methodologically addressing the bottlenecks revealed during testing, one ensures that the PHP application is not only prepared to handle high traffic but does so in an efficient manner. Continual monitoring and reiteration based on subsequent tests are equally vital to maintaining optimal performance.
Continuous Testing and Maintenance
In the dynamic landscape of web development, ensuring the performance of your PHP website doesn't just end after a single load test. It's vital to incorporate continuous testing into your development and deployment cycles to maintain optimal performance as your site evolves. This section outlines how to set up ongoing tests using LoadForge, integrate load testing into your Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipeline, and continuously address the performance of your PHP site.
Setting Up Ongoing Tests with LoadForge
Continuous load testing helps in regularly assessing the performance of your PHP website and catching issues before they impact your users. LoadForge offers features that simplify the process of scheduling and managing recurring tests:
-
Scheduled Tests: Utilize LoadForge's ability to schedule tests at regular intervals (daily, weekly, monthly). This helps ensure that your application handles the expected load, especially after updates or during critical times like sales or major releases.
To set up a scheduled test in LoadForge:
- Navigate to your test script dashboard.
- Select the locustfile you wish to schedule for continuous testing.
- Click on the "Schedule Test" option and configure the interval and start time.
-
Alerts and Notifications: Configure alerts to be notified about critical performance metrics. LoadForge can send notifications via email or webhooks if performance drops below a certain threshold.
<pre><code>
# Example webhook configuration in LoadForge
LOADFORGE_WEBHOOK_URL = "https://your-ci-server.com/loadforge-alerts"
LOADFORGE_ALERT_THRESHOLD = 5000 # users
</code></pre>
Integrating into the CI/CD Pipeline
Integrating load testing into your CI/CD pipeline allows you to automatically run tests every time changes are deployed, ensuring that recent updates do not adversely affect the site’s performance:
-
CI/CD Integration: Use the LoadForge API or CLI tools to trigger load tests as part of the deployment process in your pipeline.
Here is an example of integrating LoadForge using a generic CI tool:
# Bash script to trigger a LoadForge test
curl -X POST -H 'Authorization: Token your_api_token' \
-d 'test_id=your_test_id' \
'https://loadforge.com/api/tests/launch/'
-
Automated Performance Gates: Define performance criteria that must be met for a deployment to proceed. Implement automated rollback or halt further deployment if the test fails these criteria.
Maintaining Performance
As new features are added and changes are made to your PHP site, it's crucial to keep a close eye on how each modification affects overall performance:
-
Regular Review of Test Results: Analyze results from continuous tests to spot trends. Look for increasing response times or reduced throughput that might suggest issues or areas for optimization.
-
Optimization Based on Data: Use data from your load tests to optimize your server configurations, refine your codebase, and improve database performance. Alter cache dynamics, tweak session management settings, and more based on concrete metrics.
-
Feedback Loop: Integrate feedback from the testing phase back into development. Use performance insights to guide future development priorities and adjustments.
Incorporating continuous testing and maintenance into your development process for PHP websites not only helps in smoothing the deployment phase but also ensures a robust, user-friendly service that can scale effectively. With LoadForge, you can automate these tasks, ensuring that your site consistently delivers top-notch performance.