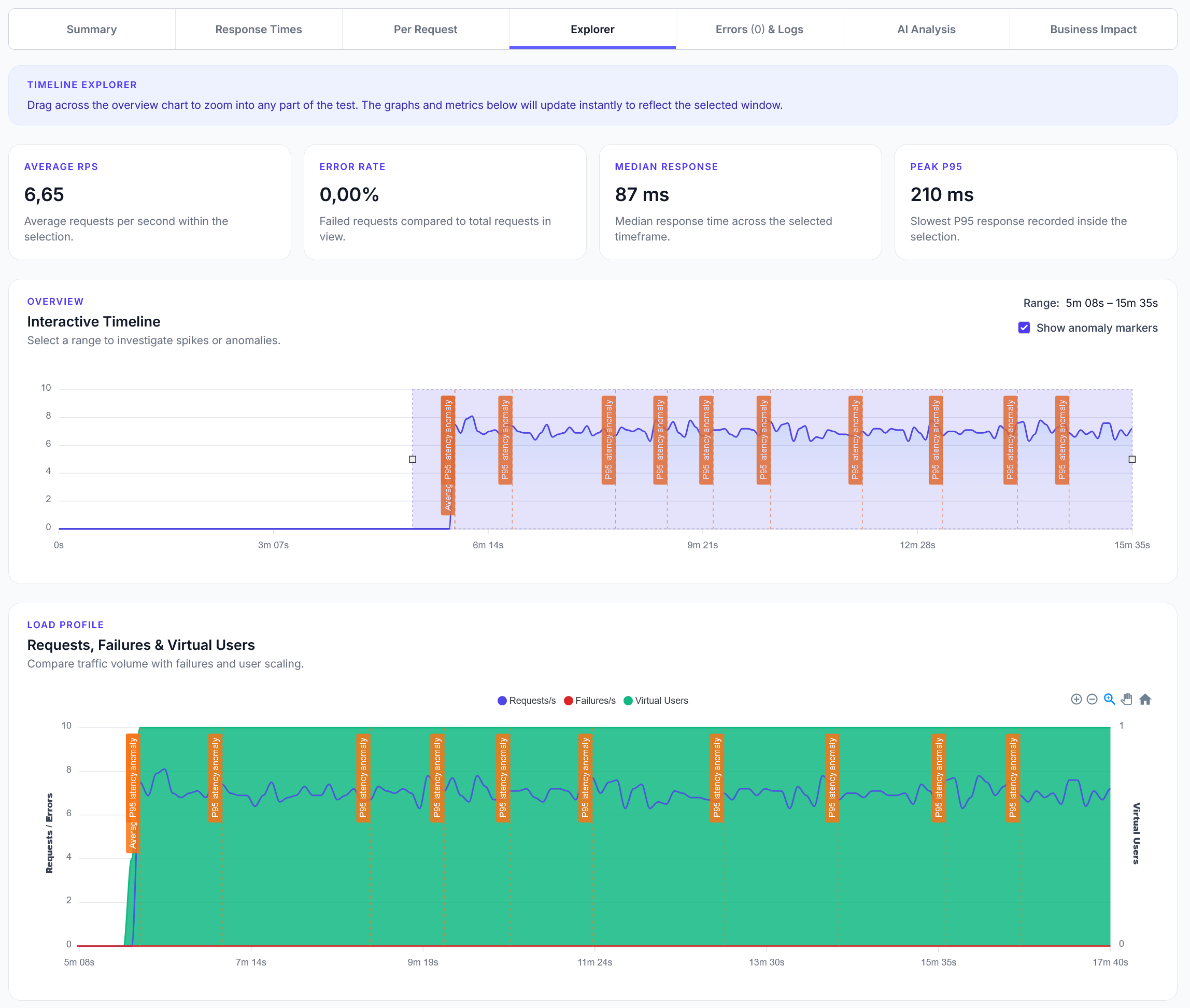
Explorer reports addition
We have added a new Explorer feature to reports, with a timeline scrubber and easy anomaly detection.
Incorporate user-like delays in your load tests using custom sleep times.
LoadForge can record your browser, graphically build tests, scan your site with a wizard and more. Sign up now to run your first test.
While testing, it's crucial to simulate user behavior as realistically as possible. One key aspect of this simulation is introducing waits or pauses that a typical user might experience, like reading a webpage or waiting for some data. By default, LoadForge's wait_time attribute allows you to set such pauses. This guide will delve deeper into customizing these waits and understanding their applications.
There are two primary ways to introduce waits in your tests:
wait_time: This attribute specifies the pause between tasks. For example, once load_page concludes, the simulated user would wait for the duration specified by wait_time before initiating the next task. In our example below, after the load_page task concludes, a user will pause for a duration anywhere between 10 to 20 seconds.
time.sleep: This function allows for more specific pauses, right at the point it's called within your test. So if you want a user to pause immediately after a particular HTTP request and before another, time.sleep can be used.
Here's an example:
import random
from locust import HttpUser, TaskSet, task, between
import time
class AwesomeUser(HttpUser):
# User waits between 10 to 20 seconds after completing each task.
wait_time = between(10, 20)
@task(1)
def load_page(self):
self.client.get('/page1')
# Here, the user waits between 10 to 60 seconds,
# simulating a pause on page1 before navigating to page2.
time.sleep(random.randint(10, 60))
self.client.get('/page2')
# This simulates that a user pauses on page2 for exactly 20 seconds.
time.sleep(20)
This test will simulate a user accessing /page1, waiting for a duration between 10 to 60 seconds (perhaps reading content or interacting with elements), and then navigating to /page2, where they pause again for a fixed 20 seconds.
LoadForge leverages the power of the open-source locust library. This means that if you're already a locust user, you can directly port this script. If you wish to amplify your testing capabilities, consider importing your script into LoadForge!